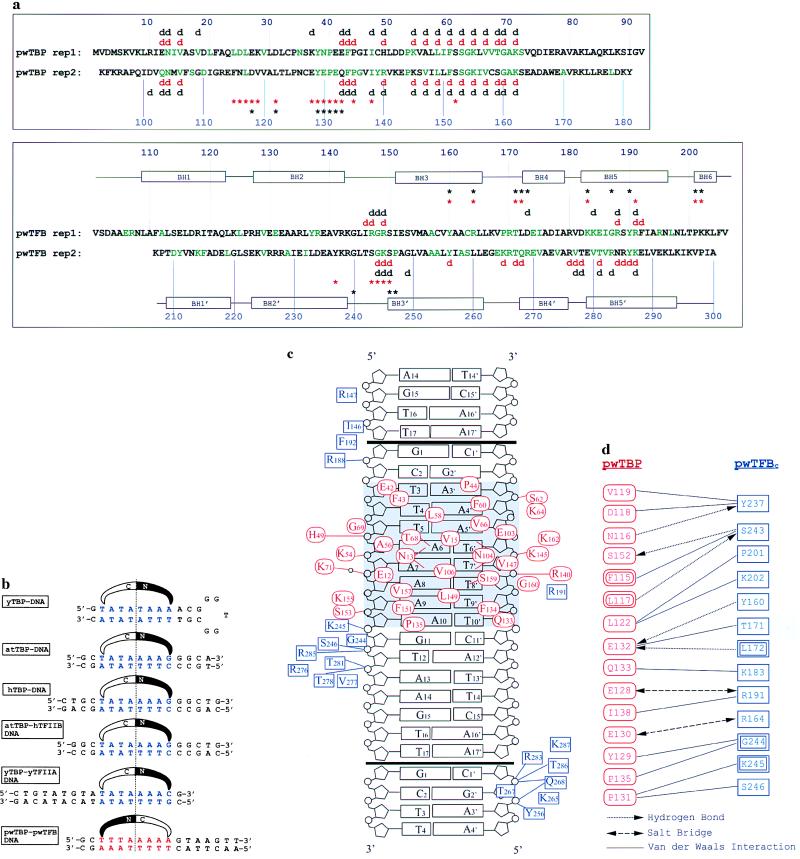
Figure 1.
(a) Amino acid sequences for pwTBP and pwTFBc. The direct repeats of pwTBP and pwTFB are aligned. pwTBP amino acids in green are conserved with Arabidopsis thaliana TBP (atTBP), and pwTFBc residues in green are conserved with human TFIIBc. Red symbols above and below the sequence indicate interactions seen in this structure (d for DNA contacts and ∗ for protein contacts). Black symbols indicate the corresponding interactions in the eukaryotic ternary structure (11). Black rectangles indicate α-helices in pwTFBc. Contacting residues are defined as having a distance < 4.0 Å. (b) Comparison of the promoter fragment crystallized in this study to five different TATA boxes seen in other TBP complex structures: yeast TBP (yTBP)–DNA (15), A. thaliana TBP (atTBP)–DNA (16, 17), human TBP (hTBP)–DNA (18), atTBP–human TFIIB–DNA (11), and yeast TBP–TFIIA–DNA (19, 20). Sequences are centered on the pseudodyad axis of the TATA box, and the orientation is shown with a schematic representation of the N-terminal and C-terminal domains of TBP. (c) Protein–DNA interactions in this structure. pwTBP residues are red ovals, and pwTFBc residues are green rectangles. The boxA/TATA element is shaded. Black bars indicate the end of the crystallization oligonucleotide. Crystal packing contacts between DNA molecules simulate a contiguous B form helix with a smaller than normal twist of 9° at the junction. This allows pwTFB to interact with phosphates of neighboring molecules in both directions. Residues involved in van der Waals interactions are shown near the region of DNA they contact. Lines indicate hydrogen bonds or salt bridge interactions. (d) Residues interacting at the pwTBP–pwTFBc interface. pwTBP residues are red and pwTFBc residues, blue. Double rectangles or ovals indicate a main-chain interaction.