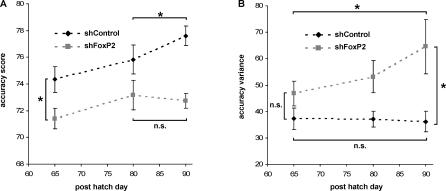
Figure 5. Differences in Song Development of FoxP2 Knockdown and Control Pupils.
(A) We measured the accuracy of syllable imitation in song recordings of the same pupils made at three different ages (PHD65, PHD80, and PHD90), using the automated batch procedure in Sound Analysis Pro. Data points represent mean values (±SEM) of 1,000–3,000 pairwise comparisons between pupil recordings and the tutor model (shFoxP2-f/-h, n = 7 animals for all ages; shControl, n = 5 animals for PHD65, n = 6 animals for PHD80, and n = 7 animals for PHD90). Syllable imitation was already less accurate in FoxP2 knockdown pupils by 65PHD (two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test, PHD65 *p < 0.05), and does not continue to improve beyond 80 d, in contrast to control pupils (two-tailed Wilcoxon signed-rank test, PHD80 to PHD90 *p < 0.05 in shControl, n.s. in shFoxP2-f/-h, p > 0.5). The dashed line connecting the data points illustrates the directionality of changes over time. but does not imply a linear relationship.
(B) Variance of syllable accuracy values increased with age in knockdown pupils, but not in controls (two-tailed Wilcoxon signed-rank test, PHD65 to PHD90 *p < 0.05 in shFoxP2-f/-h, n.s. in shControl, *p > 0.4). This leads to significantly higher variance at PH90 in knockdown pupils compared to control pupils (two-tailed Mann-Whitney U test, PHD90 *p < 0.05). Dashed lines as in (A).