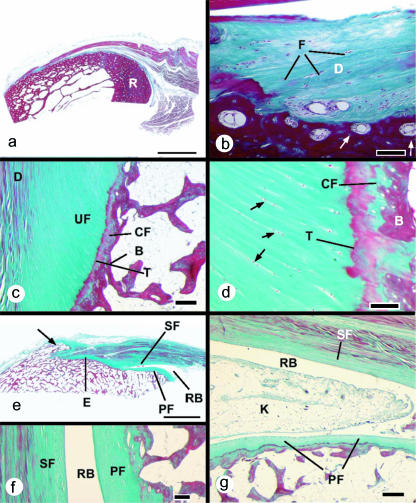
Fig. 1.
Histological sections (stained with Masson's trichrome) of entheses from dissecting room cadavers. (a) A macroscopic view of the fibrous enthesis at the insertion of pronator teres on the mid-shaft of the radius (R). Note the thick layer of cortical bone. Scale bar = 5 mm. (b) Higher magnification view of the pronator teres enthesis, showing the presence of dense fibrous connective tissue (D) at the bone–tendon junction. Fibroblasts are evident (F), but no fibrocartilage cells. Note the presence of osteons at the attachment site (arrows). Scale bar = 100 µm. (c) A typical fibrocartilaginous enthesis (Achilles tendon) showing the four zones of tissue at the bone–tendon interface: dense fibrous connective tissue (D), uncalcified fibrocartilage (UF), calcified fibrocartilage (CF) and bone (B). The two fibrocartilage zones are separated from each other by a tidemark (T). Note that the tidemark is straight, but the tendon–bone interface (i.e. the junction between calcified and non-calcified fibrocartilage) is highly irregular (arrows). This is critical for the integrity of the junction. Scale bar = 300 µm. (d) A higher magnification view of the fibrocartilage zones at the Achilles tendon enthesis. The zone of uncalcified fibrocartilage is characterized by rows of fibrocartilage cells (arrows) that are separated from each other by parallel bundles of collagen fibres. T, tidemark; B, bone. Scale bar = 100 µm. (e) A macroscopic view of the Achilles tendon enthesis organ. This consists of the enthesis itself (E), a thick periosteal fibrocartilage (PF) on the superior tuberosity (ST) of the calcaneus, a sesamoid fibrocartilage (SF) in the deep surface of the tendon, an intervening retrocalcaneal bursa (RB) and the tip of Kager's fat pad (not visible in this section). Note the enthesophyte (arrow) in the most inferior part of the enthesis. Scale bar = 5 mm. (f) A higher magnification view of the sesamoid (SF) and periosteal (PF) fibrocartilages that lie either side of the retrocalcaneal bursa (RB). Scale bar = 100 µm. (g) The wedge-shaped tip of Kager's fat pad (K) protrudes into the retrocalcaneal bursa (RB) in a plantarflexed foot. PF, periosteal fibrocartilage; SF, sesamoid fibrocartilage. Scale bar = 500 µm.