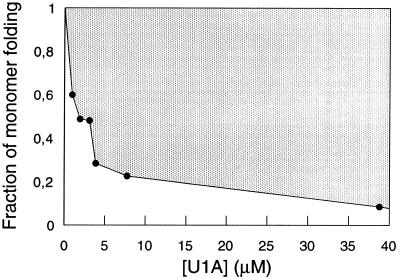
Figure 3.
Fraction of monomer folding at different concentrations of U1A, expressed as the ratio of the amplitudes of the fast and slow refolding phase (compare Fig. 2A). In fits where [U1A] ≥ 3.1 μM the rate constant for the fast phase was locked to 200 s−1. Since refolding is usually monitored at relatively high concentrations of protein, the proportion of monomer folding may be very small and undetected. For example, standard stopped-flow (≈10 μM), stopped-flow CD (10–50 μM), and quench-flow NMR (>100 μM). Hence, tests of concentration dependence in these regions may not reveal aggregation artefacts.