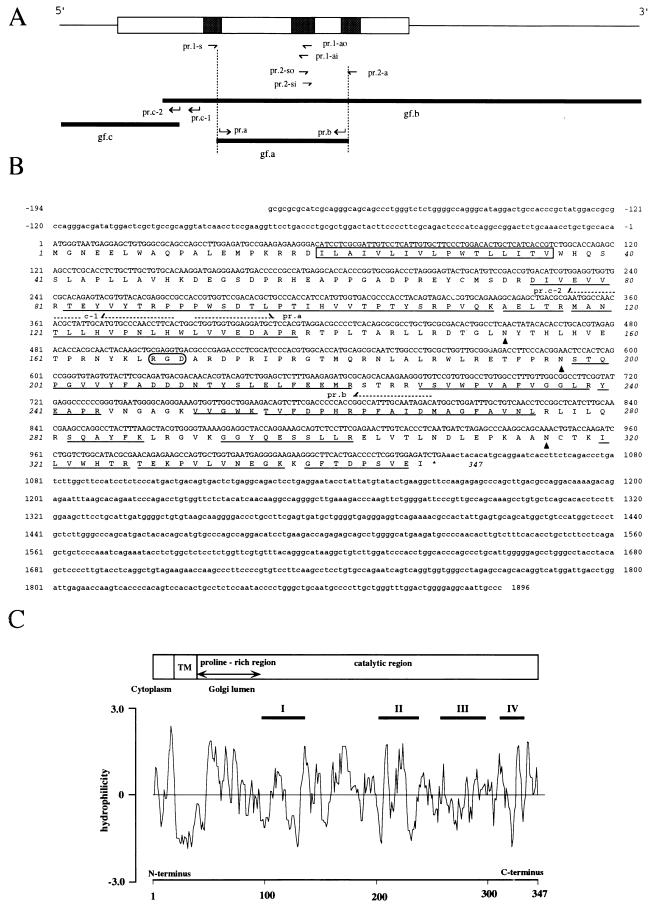
Figure 1.
(A) Strategy for full-length GlcAT-P cDNA cloning. The upper bar is the overall structure of the GlcAT-P cDNA. Thin line and column indicate the noncoding and coding regions, respectively. The peptides used for generating degenerated primers are shown as shaded boxes in the column. Based on the amino acid sequences, six mixed oligonucleotide primers (prs.1-s, 1-ao and -ai, and prs.2-so, si, and 2-a) were designed. Hocked arrows (pr.a, pr.b, pr.c-1, and pr.c-2) indicate the positions and directions of completely matched primers. The nucleotide sequences of these primers are shown in B. gfs a, b, and c indicate partial cDNA fragments of GlcAT-P. (B) Nucleotide and deduced amino acid sequences of the GlcAT-P. Amino acid residues determined by the peptide sequencer are underlined. The putative transmenbrane region is boxed. The potential N-glycosylation sites are indicated by arrow heads. The dashed arrows indicate the position and direction of primers used for the cDNA cloning. (C) Hydropathy analysis of the GlcAT-P. The distribution of hydrophobic and hydrophilic regions were analyzed by the method of Hopp and Woods (26). The predicted domain structure is described on the top of the figure.