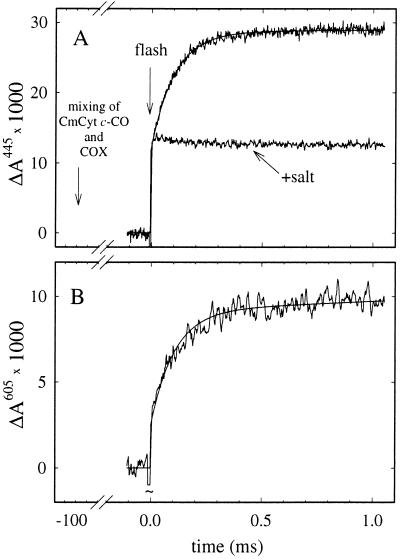
Figure 3.
(A) Absorbance changes after pulsed illumination of the ferro CmCyt c-CO complex about 100 ms after mixing with an anaerobic solution of cytochrome c oxidase (COX) (upper trace). The rapid initial increase in absorbance is due to CO dissociation. The following slower increase is associated with oxidation of CmCyt c and reduction of Fea. It was fit with an exponential function with a rate constant of 9,700 s−1 (solid noise-free line). The lower trace was recorded after addition of KCl to a concentration of ≈300 mM to the CmCyt c solution before the experiment. (B) Same experiment as upper trace in A but recorded at 605 nm. At this wavelength there is essentially no contribution from oxidation of ferro-CmCyt c (see Fig. 1). A laser artifact at t = 0 has been truncated. The ratio of the absorbance changes at 445 nm and 605 nm is consistent with reduction of heme a during the 9,700 s−1 phase. Conditions after mixing: 0.55 μM photoactive CmCyt c, 2.5 μM cytochrome c oxidase, 0.1 mM CO, 0.1% dodecyl maltoside, 10 mM Hepes, pH 7.1, 22 ± 1°C.