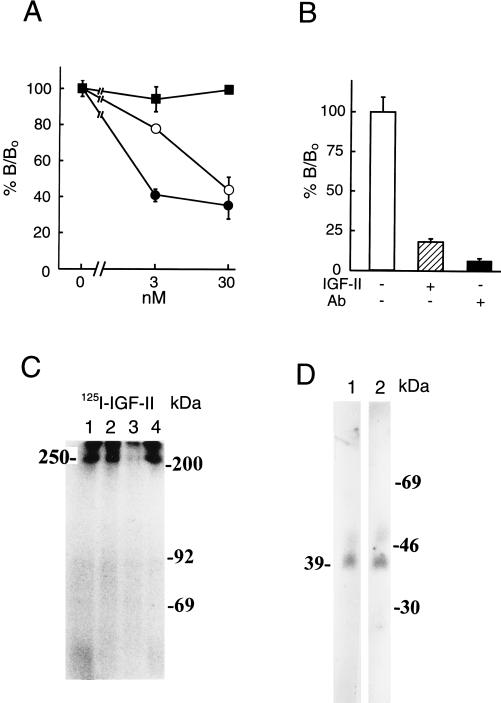
Figure 1.
Presence of IGF-II/M-6-P-receptor in pancreatic β cells. Cell binding assays (A) were performed in triplicate using 125I-IGF-II in the presence (3 or 30 nM) or absence of unlabeled IGF-I (○), IGF-II (•), or insulin (▪). The results are presented as the means ± SD. Binding was evaluated as the percentage of IGF-II bound (B/B0; B corresponding to observed binding and B0 to total binding of labeled IGF-II). In B blocking capacity of an anti-IGF-II/M-6-P receptor antibody on IGF-II binding to the cells was evaluated. Experimental conditions were as indicated in the figure. A and B show one representative experiment out of two, respectively. For affinity crosslinking (C), cells were incubated with 125I-IGF-II, in the absence (lane 1) or presence (lane 2) of 100 nM IGF-I, IGF-II (lane 3), or insulin (lane 4) and crosslinked with disuccinimidyl suberate. Affinity-labeled proteins were separated by SDS/PAGE under reducing conditions. Positions of the protein molecular mass standards are shown (in kilodaltons). IGFBPs secreted from the cells were investigated with Western ligand blotting of conditioned media (D), using labeled IGF-I (lane 1) or IGF-II (lane 2). Positions of protein molecular mass standards are shown in kilodaltons. In C and D, a representative experiment out of three and two, respectively, is shown.