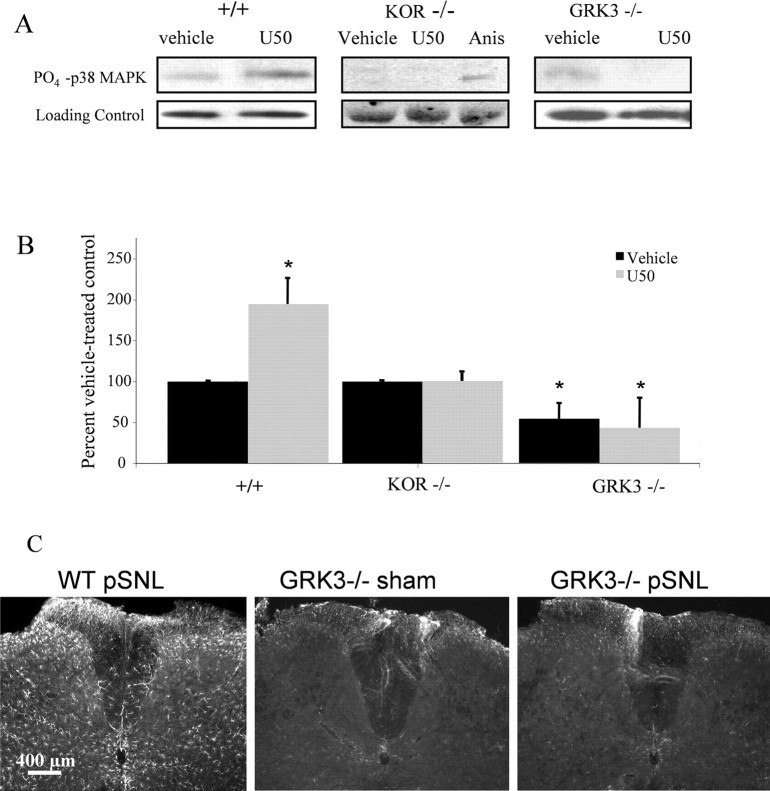
Figure 9.
agonist activation enhances phospho-p38 MAPK-IR in primary astrocyte cultures by a mechanism requiring GRK3. A, Representative gels showing phospho-p38-IR after U50,488 (U50) treatment in cell lysates prepared from spinal cord astrocytes cultured from WT (+/+), KOR−/−, or GRK3−/− mice. Top, Phospho-p38-IR; bottom, loading control; Anis, anisomycin. B, U50,488 treatment of WT astrocytes (left bars) increased phospho-p38 MAPK-IR to 195 ± 32% of vehicle-treated controls. In contrast, phospho-p38-IR in KOR−/− astrocyte cultures did not change after 1 μm U50,488 treatment (middle bars). Basal phospho-p38-IR in GRK3−/− astrocyte cultures was significantly lower than in GRK3+/+ astrocytes (*p < 0.05), and phospho-p38-IR did not significantly increase in GRK3−/− cultures after U50,488 treatment [right bars, 54 ± 20% (black) and 43 ± 37% (gray) of WT (+/+) vehicle-treated controls, respectively] (*p < 0.05 compared with vehicle-treated WT (+/+) controls; n = 6–10 replicates). C, Consistent with the lack of U50,488-induced increase in phospho-p38 in astrocyte cultures, GRK3−/− mice did not increase GFAP-IR in lumbar spinal cord 7 d after pSNL.