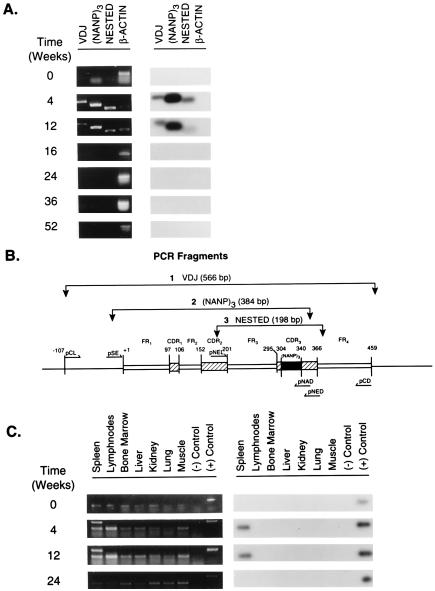
Figure 2.
PCR amplification and Southern blot hybridization to detect the presence of the transgene H chain in vivo. (A) Presence of the transgene in splenic genomic DNA at various times after DNA inoculation. Spleens were harvested 4, 12, 16, 24, 36, and 52 wk after DNA inoculation. The spleen of a naive mouse served as a negative control and is referred to as time 0. Detection of the transgene in the genomic DNA was performed by PCR amplification using three sets of primers (pCL/pCD, pSE/pNAD, and pNEL/pNED) specific for three different DNA fragments of plasmid DNA γ1NANP and confirmed by Southern blot hybridization using the 32P-labeled pNAD oligonucleotide. The location and size of the PCR fragments [VDJ, (NANP)3, and NESTED] are illustrated in Fig. 2B. A PCR fragment identified as β-actin (for the murine β-actin gene) served as an internal control. Left, the results of PCR amplification. Right, the results of Southern blot hybridization. B is a schematic representation of the VH gene contained in plasmid DNA γ1NANP. The annealing sites of the primers, the predicted amplification fragments and their molecular size, are identified: FR, framework region; VDJ refers to a fragment that is inclusive of the coding region for the rearranged VDJ gene segments; (NANP)3 refers to a 384-bp fragment containing in the CDR3 of the VH region the sequence coding for three repeats of the tetrapeptide Asn-Ala-Asn-Pro between nucleotides 304 and 340 (32); NESTED refers to a 198-bp fragment inclusive of the coding region for FR3 and the CDR3. +1 refers to the first nucleotide in the coding region of FR1. Any other position in the gene is numbered in reference to nucleotide +1. (C) Tissue distribution of the transgene in vivo. Genomic DNA was extracted from the tissues listed. Tissues were obtained at various times from DNA inoculation. Tissues from a naive mouse refers to time 0. Left, PCR amplification of the VDJ fragment of the transgene using the primers pCL/pCD. Right, results of Southern blot hybridization using the 32P-labeled pNAD oligonucleotide. {/TITL;;;center;stack}