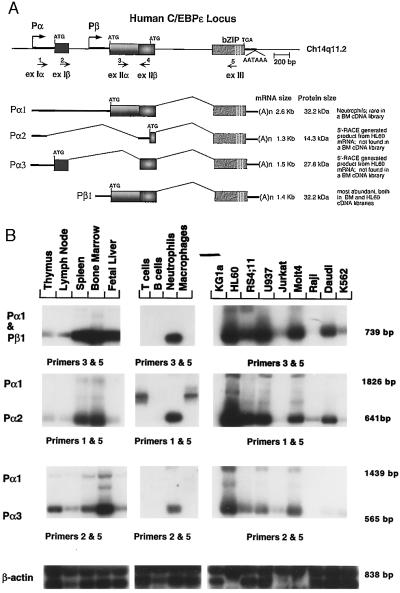
Figure 1.
Modular structure of the C/EBPɛ gene and its distinct RNA transcripts. (A) The transcription start sites of each of the two promoters, Pα and Pβ, are indicated by arrows. Boxes represent coding regions and thick lines represent untranslated regions of the mature mRNA. Nos. 1–5 correspond to primers RY46, RY44, RY66, RY68, and RY77, respectively. The location of the relevant start codons for each transcript and the common TGA stop codon is also shown. Vertical lines in the bZIP region indicate the presence of the leucine repeat. (B) RT-PCR reaction products amplified by the combination of C/EBPɛ specific primers indicated for each panel were analyzed by Southern blotting, using an internal primer as a probe (primer 4, A). All products were verified by sequence. β-Actin specific primers were used as controls. Fragment sizes are shown on the right, and the name of each transcript is at the left. The combination of primers 1 and 5 in primary T cells and macrophages amplifies a crossreacting product that is not related to epsilon based on sequence analysis of this fragment (Middle). A Pα1 RT-PCR-generated fragment of 1,826 bp is detected with longer exposure times in neutrophils (not shown).