Abstract
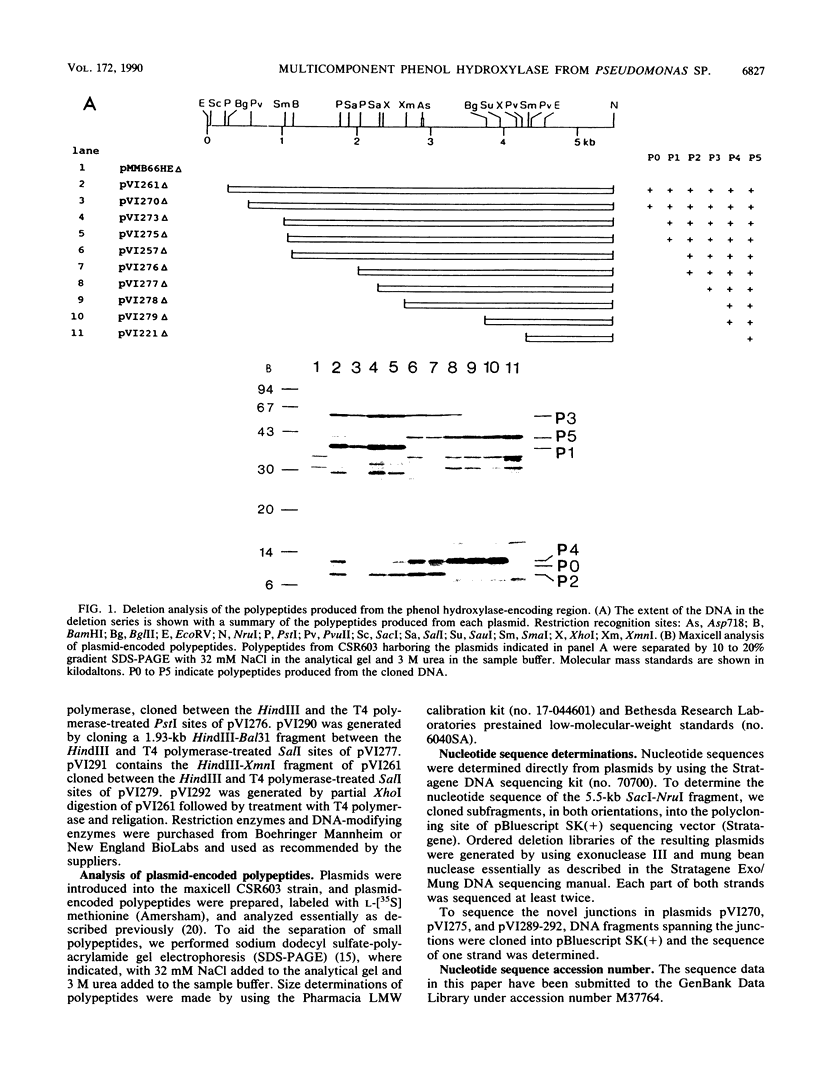
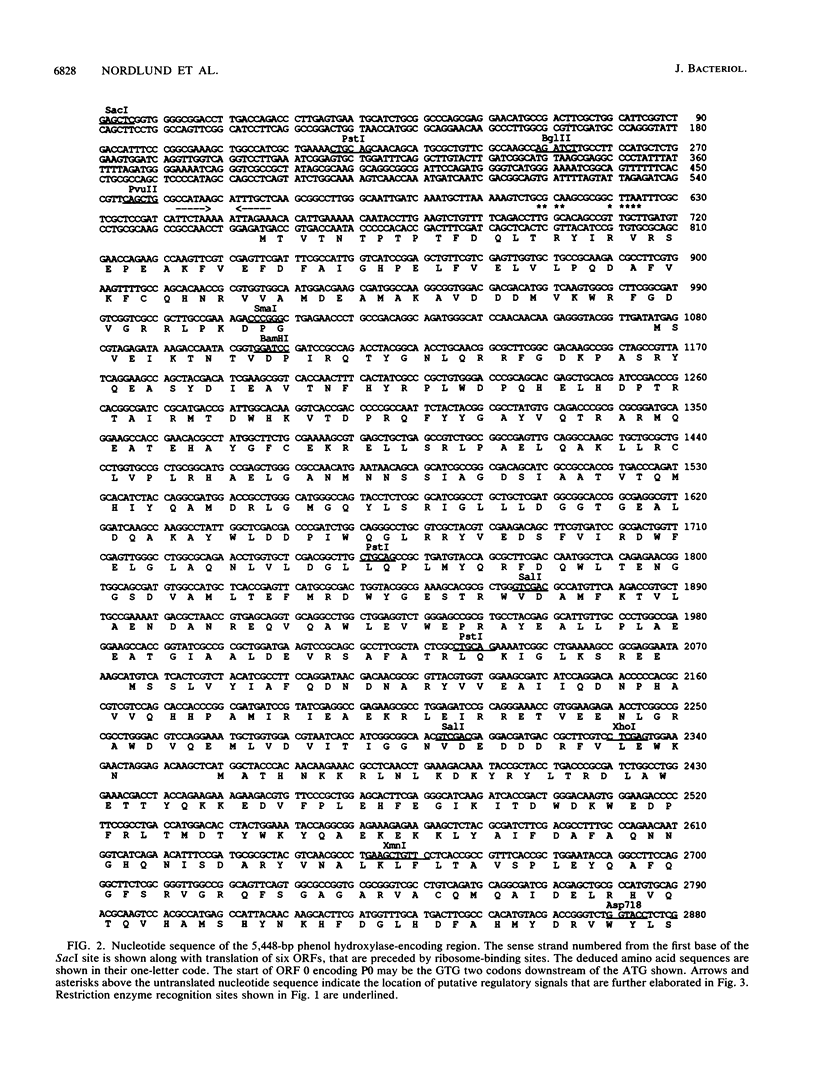
Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600 metabolizes phenol and some of its methylated derivatives via a plasmid-encoded phenol hydroxylase and meta-cleavage pathway. The genes encoding the multicomponent phenol hydroxylase of this strain are located within a 5.5-kb SacI-NruI fragment. We report the nucleotide sequence and the polypeptide products of this 5.5-kb region. A combination of deletion analysis, expression of subfragments in tac expression vectors, and identification of polypeptide products in maxicells was used to demonstrate that the polypeptides observed are produced from the six open reading frames identified in the sequence. Expression of phenol hydroxylase activity in a laboratory Pseudomonas strain allows growth on phenol, owing to expression of this enzyme and the chromosomally encoded ortho-cleavage pathway. This system, in conjunction with six plasmids that each expressed all but one of the polypeptides, was used to demonstrate that all six polypeptides are required for growth on phenol.
Full text
PDF





Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bartilson M., Nordlund I., Shingler V. Location and organization of the dimethylphenol catabolic genes of Pseudomonas CF600. Mol Gen Genet. 1990 Jan;220(2):294–300. doi: 10.1007/BF00260497. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bartilson M., Shingler V. Nucleotide sequence and expression of the catechol 2,3-dioxygenase-encoding gene of phenol-catabolizing Pseudomonas CF600. Gene. 1989 Dec 21;85(1):233–238. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(89)90487-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dixon R. The xylABC promoter from the Pseudomonas putida TOL plasmid is activated by nitrogen regulatory genes in Escherichia coli. Mol Gen Genet. 1986 Apr;203(1):129–136. doi: 10.1007/BF00330393. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürste J. P., Pansegrau W., Frank R., Blöcker H., Scholz P., Bagdasarian M., Lanka E. Molecular cloning of the plasmid RP4 primase region in a multi-host-range tacP expression vector. Gene. 1986;48(1):119–131. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(86)90358-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Ebina Y., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Nucleotide sequence surrounding transcription initiation site of xylABC operon on TOL plasmid of Pseudomonas putida. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1688–1691. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1688. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Inouye S., Nakazawa A., Nakazawa T. Overproduction of the xylS gene product and activation of the xylDLEGF operon on the TOL plasmid. J Bacteriol. 1987 Aug;169(8):3587–3592. doi: 10.1128/jb.169.8.3587-3592.1987. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler T., Harayama S., Ramos J. L., Timmis K. N. Involvement of Pseudomonas putida RpoN sigma factor in regulation of various metabolic functions. J Bacteriol. 1989 Aug;171(8):4326–4333. doi: 10.1128/jb.171.8.4326-4333.1989. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nordlund I., Shingler V. Nucleotide sequences of the meta-cleavage pathway enzymes 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde dehydrogenase and 2-hydroxymuconic semialdehyde hydrolase from Pseudomonas CF600. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1990 Jun 21;1049(2):227–230. doi: 10.1016/0167-4781(90)90046-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Platt T. Transcription termination and the regulation of gene expression. Annu Rev Biochem. 1986;55:339–372. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.55.070186.002011. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Powlowski J., Shingler V. In vitro analysis of polypeptide requirements of multicomponent phenol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas sp. strain CF600. J Bacteriol. 1990 Dec;172(12):6834–6840. doi: 10.1128/jb.172.12.6834-6840.1990. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sancar A., Hack A. M., Rupp W. D. Simple method for identification of plasmid-coded proteins. J Bacteriol. 1979 Jan;137(1):692–693. doi: 10.1128/jb.137.1.692-693.1979. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shine J., Dalgarno L. Determinant of cistron specificity in bacterial ribosomes. Nature. 1975 Mar 6;254(5495):34–38. doi: 10.1038/254034a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shingler V., Franklin F. C., Tsuda M., Holroyd D., Bagdasarian M. Molecular analysis of a plasmid-encoded phenol hydroxylase from Pseudomonas CF600. J Gen Microbiol. 1989 May;135(5):1083–1092. doi: 10.1099/00221287-135-5-1083. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zylstra G. J., Gibson D. T. Toluene degradation by Pseudomonas putida F1. Nucleotide sequence of the todC1C2BADE genes and their expression in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989 Sep 5;264(25):14940–14946. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





