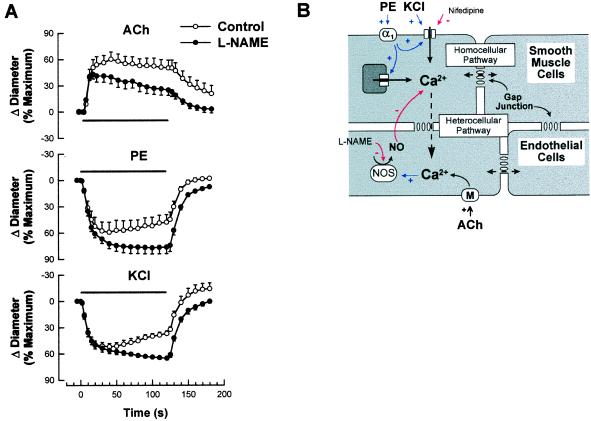
Figure 5.
(A) Effect of l-NAME on the time course of changes in vessel diameter in response to agonists. ACh (10−4 M, n = 5), PE (10−5 M, n = 5), and KCl (250 mM, n = 5) were pressure-pulse ejected adjacent to a segment of the arteriole for a period of 2 min (▪). l-NAME (10−5 M) was added to the superfusion solution and allowed to equilibrate for 20 min, and had no effect on vessel diameter (Δ Diameter from 64.5 ± 3.4 to 66.8 ± 3.4 μm, n = 15). Without changing the stimulation pipette position, the time course for each agonist was repeated in the presence of l-NAME. Values are means ± SE of paired responses before and after l-NAME. (B) Schematic of the proposed heterocellular Ca2+ diffusion pathway. Increases in smooth muscle [Ca2+]i stimulated by either PE or KCl diffuse radially to underlying endothelial cells through myoendothelial gap junctions. The secondary increase in endothelial cell [Ca2+]i stimulates NO synthase to generate NO and modulate smooth muscle [Ca2+]i and hence contraction. The extent of homocellular Ca2+ diffusion is limited by cell volume and distance.