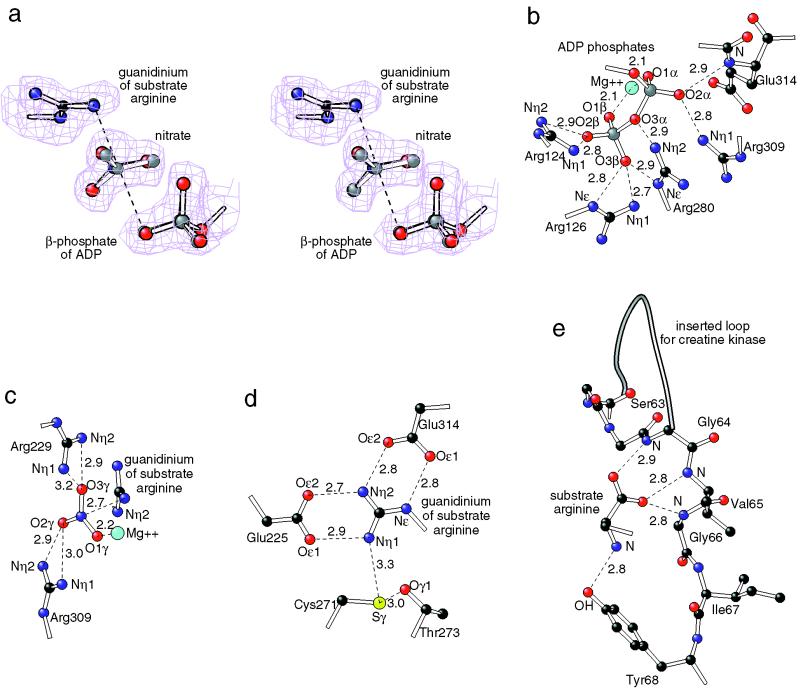
Figure 2.
Details of the active site. For clarity only atoms in the immediate neighborhood are shown with carbon-colored black, oxygen red, nitrogen dark blue, magnesium light blue, sulfur yellow and phosphorus gray. Distances are shown in Å. (a) Stereo diagram comparing part of the experimental analog structure with omit-map electron density and the structure of the presumptive transition state (gray atoms). Small molecule model systems suggest a preassociative concerted phosphoryl transfer and a pentavalent γ-phosphorus transition state with about 20% covalent bonding to both the β-phosphoryl oxygen and guanidino nitrogen (32, 33). The transition-state coordinates were derived from the experimental coordinates by replacing the nitrate with a phosphoryl group, and refining with additional distance and angle restraints appropriate for the estimated 20% partial covalent bonding. (b–e) Details of the enzyme-substrate analog interactions: (b) α and β phosphoryl groups of the ADP are held in place by extensive hydrogen bonds/salt bridges with four highly conserved arginines; (c) the nitrate (mimicking a planar phosphoryl group during transfer) is sandwiched between two conserved arginines and the Mg2+ ion whose position is constrained by ligands from the α and β phosphoryl groups of the ADP; (d) the guanidinium of the substrate arginine is clamped with salt bridges/hydrogen bonds to two carboxylates and a conserved cysteine that likely exists as a thiolate (54); and (e) interactions of the substrate amino and carboxylate groups with loop residues 63–68 of the enzyme. The carboxylate-to-backbone interactions might be conserved between all phosphagens and their kinases. The amino groups are present in arginine and lombricine but absent from creatine and glycocyamine. The tyrosine interacting with the amino group is conserved among AKs, but is a valine in all other phosphagen kinases. Immediately preceding residue 61 (and interactions with the carboxylate) is an insertion in other sequences whose size inversely correlates with the size of substrate (42).