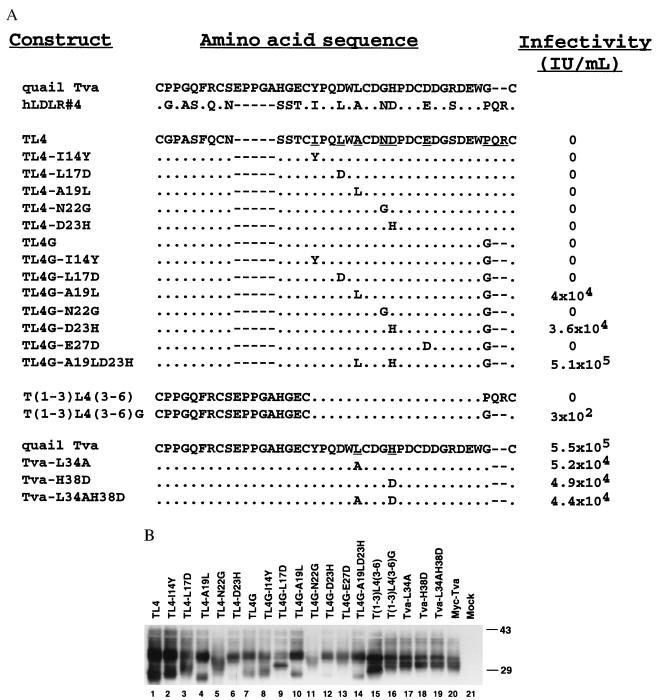
Figure 2.
Sequences, expression, and function of Tva/hLDL-A4 chimeras and Tva mutants. (A) Sequences of the chimeric receptors and mutants along with analysis of their ability to mediate RSV(A) infection. Alignment of the Tva LDLR module and hLDL-A4 is shown at the top (dot, identical residue; dash, gap). The LDLR module of Tva was replaced with human LDL-A4 to generate TL4. Below the TL4 sequence are the series of mutants that were generated based on this chimera as described in the text. The nine nonconserved residues in TL4 targeted for mutation are underlined. At the bottom is the quail Tva sequence and sequences of three mutations in Tva described in the text. The ability of the chimeras and mutants to mediate RSV(A) infection was assayed by using an RCAS(A)-AP vector and is expressed as the number of positive AP-staining cells per milliliter of viral stock (IU/ml). (B) Transient expression of Tva/hLDL-A4 chimeras and Tva mutants in 293T cells. Lysates from 293T cells expressing Tva/hLDL-A4 chimeras were subjected to SDS/PAGE, and the Western blot was probed with a monoclonal anti-myc antibody.