Table 2.
Kinetics of refolding and unfolding of wild-type and mutant CI2
| CI2 protein | kfH2O*, s−1 | mkf†, M−1 | ΔΔG‡-DH2O‡ kcal mol−1 | kuH2O*, ×104 s−1 | mku†, M−1 | ΔΔG‡-NH2O‡ kcal mol−1 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Wild type | 56.5 ± 2.5 | −1.82 ± 0.12 | — | 1.2 ± 0.1 | 1.31 ± 0.01 | — |
| Mutations at the C terminus of the helix | ||||||
| KR18 | 66.0 ± 2.4 | −1.91 ± 0.05 | −0.09 ± 0.03 | 1.2 ± 0.2 | 1.26 ± 0.03 | −0.01 ± 0.11 |
| KR18/DR23 | 89.8 ± 3.6 | −2.10 ± 0.06 | −0.27 ± 0.04 | 28 ± 3 | 1.27 ± 0.02 | −1.87 ± 0.01 |
| DA23 | 83.9 ± 1.7 | −2.16 ± 0.06 | −0.23 ± 0.03 | 3.8 ± 0.9 | 1.38 ± 0.04 | −0.69 ± 0.05 |
| Mutations in the protease-binding loop region | ||||||
| RF48 | 2300 ± 200 | −1.89 ± 0.04 | −2.18 ± 0.06 | n.d. | n.d. | −0.75 ± 0.02§ |
| RF48/FL50 | 375 ± 10 | −1.92 ± 0.03 | −1.12 ± 0.03 | 18 ± 3 | 1.14 ± 0.03 | −1.59 ± 0.10 |
The rates of folding, kfH2O, and unfolding, kuH2O, of the protein were measured as described (6). The values of kfH2O measured directly in water (data not shown) and those derived by extrapolation from GdmCl (shown here) are identical within experimental error.
mkf and mku are calculated from the denaturant dependency of the folding and unfolding rate constants according to: ln kf[GdmCl] = ln kfH2O + mkf [GdmCl] and ln ku[GdmCl] = ln kuH2O + mku [GdmCl].
ΔΔG‡-DH2O and ΔΔG‡-NH2O are the changes in free energies of activation of folding and unfolding, respectively, relative to the wild-type protein. They are calculated according to ref. 6.
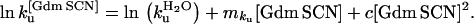 |
The kinetic parameters were calculated at 4 M Gdm SCN. Wild-type CI2 unfolds with a rate constant of 31.5 ± 1 s−1 in 4 M Gdm SCN relative to 113 ± 3 s−1 for RF48 CI2. We can thus calculate ΔΔG‡-D4M Gdm SCN for the RF48 CI2 mutant to be −0.75 ± 0.02 kcal mol−1. The unfolding mku[Gdm SCN]-values in Gdm SCN are 1.69 ± 0.03 M−1 and 1.58 ± 0.04 M−1, for wild-type CI2 and RF48 CI2 respectively.
GdmCl, guanidine hydrochloride; Gdm SCN, guanidinium isothiocyanate.
