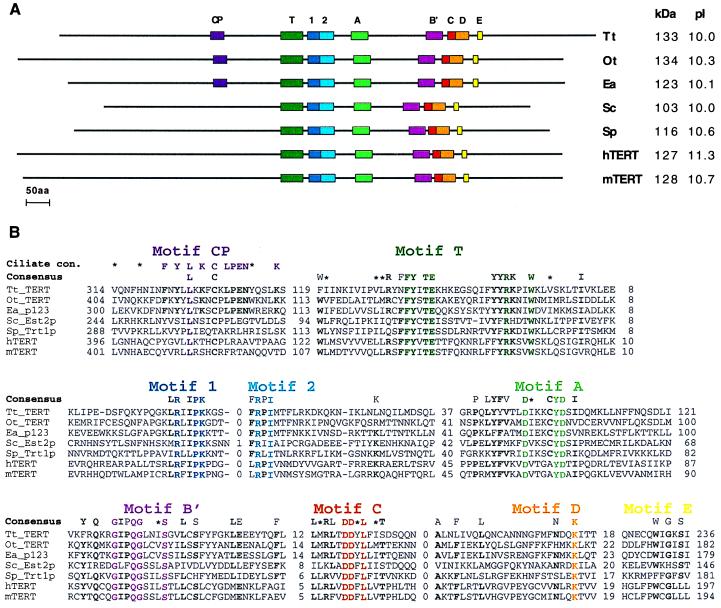
Figure 1.
Primary structure of the seven known telomerase RTs. Organisms represented are Tetrahymena thermophila (Tt_TERT; this paper), Oxytricha trifallax (Ot_TERT; this paper), Euplotes aediculatus [Ea_p123; (25)], Saccharomyces cerevisiae [Sc_Est2p; (26)], Schizosaccharomyces pombe [Sp_Trt1p; (20)], Homo sapiens [hTERT; (20)], and Mus musculus [mTERT; (30)]. (A) Colored boxes indicate the locations of RT motifs 1, 2 and A to E (41), telomerase-specific motif T (20), and the new motif found in ciliated protozoa, CP. kDa, molecular mass in kilodaltons; pI, isoelectric point. (B) Multiple sequence alignment of the motif amino acid sequences. Distances (in amino acids) between motifs and to the ends of the protein are shown. A consensus derived from all seven sequences is shown above them. Amino acids are included in the consensus if they appear in at least five sequences and are typed in bold if the remaining amino acids are conservative substitutions. Colored residues are conserved throughout all seven sequences. ∗, Amino acid similarity. A consensus derived from just the three ciliated protozoa sequences also is shown for motif CP. Abbreviations for the amino acids are as follows: A, Ala; C, Cys; D, Asp; E, Glu; F, Phe; G, Gly; H, His; I, Ile; K, Lys; L, Leu; M, Met; N, Asn; P, Pro; Q, Gln; R, Arg; S, Ser; T, Thr; V, Val; W, Trp; and Y, Tyr. The nucleotide sequences of the T. thermophila and O. trifallax genes have been submitted to GenBank (accession nos. AF062652 and AF060230, respectively).