Figure 2. zip exhibits an orientation phenotype.
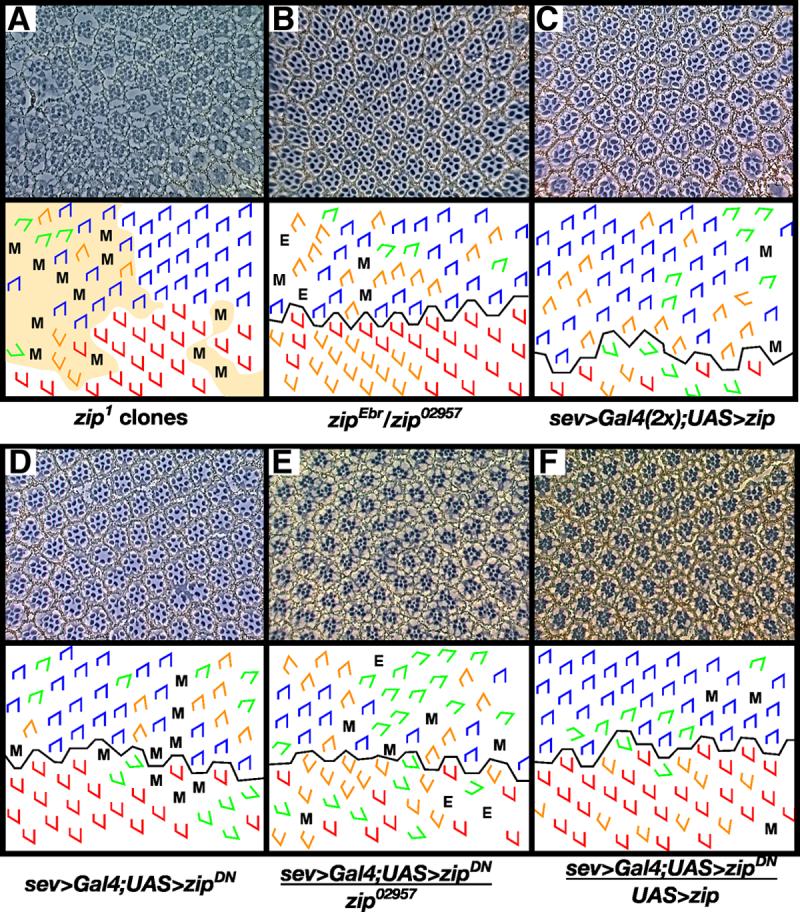
Clones of the null allele zip1 (A) and hypomorphic transheterozygous flies (zipEbr/zip02957) (B) exhibit rotation errors. In (A), shaded area denotes regions of phenotypically mutant tissue, presumably a consequence of loss of zip mutant cells since no w- photoreceptors can be identified. Misexpression of zip (C) and zipDN (D) under the sev promoter results in defects in ommatidial rotation. To demonstrate the efficacy of the sev>zipDN transgene, zip dosage was decreased (E) or increased (F) in a sev>zipDN background. Decreasing zip dosage using zip02957 enhances the sev>zipDN phenotype (E) whereas increasing zip dosage using a second copy of the UAS>zip transgene suppresses the sev>zipDN phenotype. M, missing photoreceptors; E, extra photoreceptors; blue trapezoids: dorsal ommatidia; red trapezoids: ventral ommatidia; green trapezoids: under-rotated ommatidia; orange trapezoids: over-rotated ommatidia.
