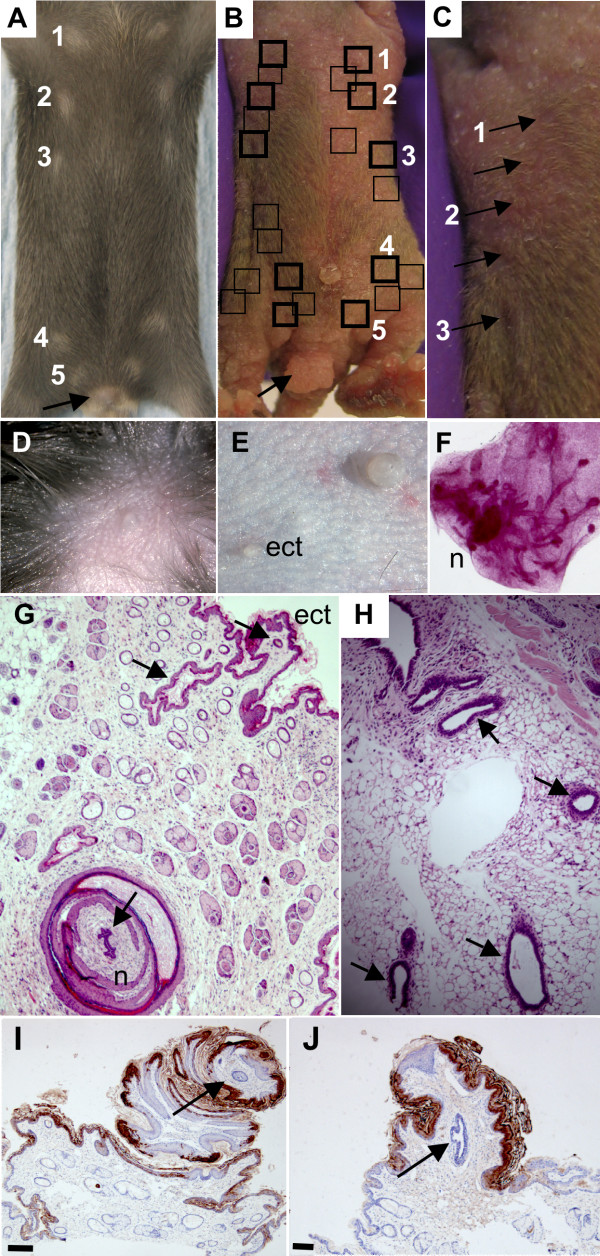
Figure 4.
Ectopic expression of Nrg3 in the epidermis results in the formation of ectopic nipples and mammary glands. (A) Ventral surface of non-transgenic littermate at P12 with the five pairs of nipples marked. Numbers denote the positions of the five normal nipples. External genitalia of female non-transgenic littermate is indicated with an arrow. (B) Ventral surface of one chimeric founder female at P12 with the five pairs of endogenous nipples boxed in bold, and ectopic nipples are marked with black boxes. Numbers denote the positions of the five normal nipples. Enlarged external genitalia of K14-Nrg3 female is indicated with an arrow. (C) Magnification of left side of (B) showing close-up of nipples which are denoted by arrows. Numbers denote the position of the endogenous nipples 1–3. (D) Non-transgenic nipples are small and round. Image acquired at 160× magnification.(E) Transgenic K14-Nrg3 nipples are very large and round. Ectopic nipples are usually smaller than the endogenous transgenic nipples and of a similar size to non-transgenic nipples. Ectopic nipple is indicated (ect). Image acquired at 160× magnification. (F) Carmine-stained whole-mount of mammary fat pad associated with ectopic nipple showing nipple (n) connected to a mammary ductal tree.(G) H&E-stained section of ectopic nipple showing associated mammary epithelial tissue. Endogenous nipple (n) and ectopic nipple (ect) are indicated and associated epithelial ducts are denoted by arrows. (H) H&E-stained section of fat pad and mammary ducts (indicated with arrows) associated with an ectopic nipple (shown in (G)). (I) K2e, a marker of nipple skin, is expressed in the endogenous K14-Nrg3 nipple skin. The primary mammary duct is indicated by an arrow. The scale bar represents 50 μm. (J) K2e, a marker of nipple skin, is expressed in the ectopic K14-Nrg3 nipple skin. The primary mammary duct is indicated by an arrow. The scale bar represents 50 μm.