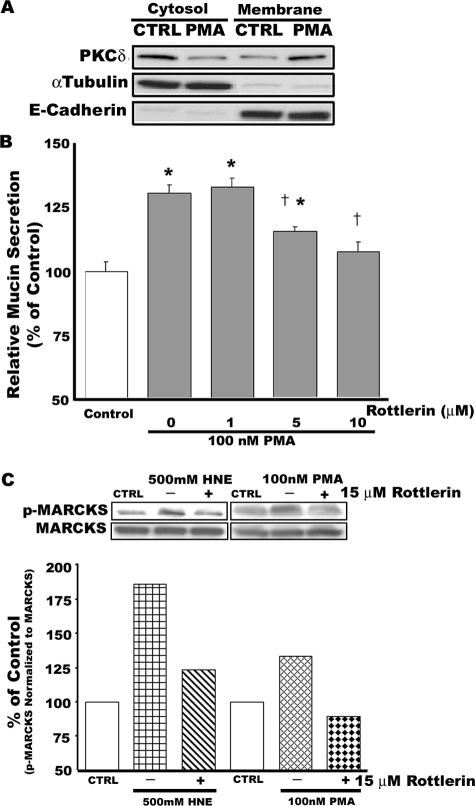
Figure 1.
Rottlerin, a selective PKCδ inhibitor, attenuates PMA-induced mucin secretion and phosphorylation of MARCKS in well differentiated NHBE cells. Cells were preincubated with 15 μmol/L rottlerin (or dimethyl sulfoxide solvent control) for 20 minutes before addition of 100 nmol/L PMA (B and C) or 500 nmol/L HNE (C). A: PKCδ translocates from cytosol to membrane in response to PMA (100 nmol/L) at 15 minutes. After detecting PKCδ, the polyvinylidene difluoride membrane was stripped and reprobed with antibodies against α-tubulin and E-cadherin, which were used as controls to detect the cytosolic and the membrane fraction, respectively. B: Rottlerin significantly attenuates PMA-induced mucin secretion in a concentration-dependent manner. *Significantly different from vehicle control (P < 0.05); †significantly different from PMA alone (P < 0.05). Data are presented as mean ± SEM (n = 4). C: Rottlerin attenuates phosphorylation of MARCKS in NHBE cells exposed to two different mucin secretagogues, HNE (500 nmol/L) or PMA (100 nmol/L). Phosphorylated MARCKS was detected by Western blot using a specific antibody against MARCKS phosphorylated at serine 152/156. After detecting phosphorylated MARCKS, the polyvinylidene difluoride membrane was stripped and reprobed with an antibody against total MARCKS protein as a loading control for each lane. Blots are representative of two replicate experiments. Densitometry measurements of the band intensities were quantified using LabWorks (BioImaging Systems, UVP, Inc., Cambridge, UK) and are shown below the blots.