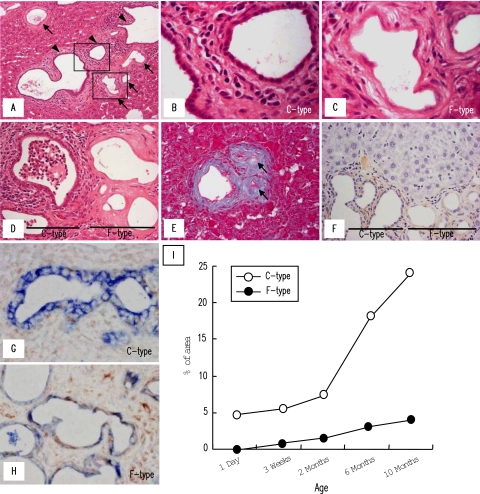
Figure 1.
Two different types of intrahepatic bile ducts of the PCK rat. Intrahepatic bile ducts of the PCK rat consisted of bile ducts lined by cuboidal-shaped cholangiocytes (C-type) (A, arrowheads, and B) and those lined by flat-shaped cholangiocytes (F-type) (A, arrows, and C). B and C: High-power views of the squares outlined in A. D: Cholangitis with polymorphonuclear cell accumulation in the lumen was a frequent histological finding in C-type, whereas F-type never associated with suppurative inflammation. E: F-type occasionally showed fibrous scar-like appearance in the elderly rats (arrows). F: Immunostaining of α-SMA using PCK liver sections. G and H: Double immunostaining of pan-CK (colored by the Vector blue reaction) and vimentin (colored by the benzidine reaction) for the PCK livers. C-type bile ducts showed single-positive signal for pan-CK (G), whereas F-type bile ducts showed double-positive signals for pan-CK and vimentin with reduced expression of pan-CK (H). I: Frequency of distribution of C- and F-type bile ducts in the PCK liver. Morphometric analysis of the stained liver sections was performed as described in Materials and Methods. Representative photographs of the 6-month-old (A--C, G, H) and 10-month-old (D--F) PCK rats. A--D, H&E; E, Azan-Mallory. Original magnifications: ×200 (A); ×400 (D–F); ×1000 (B, C, G, H).