Abstract
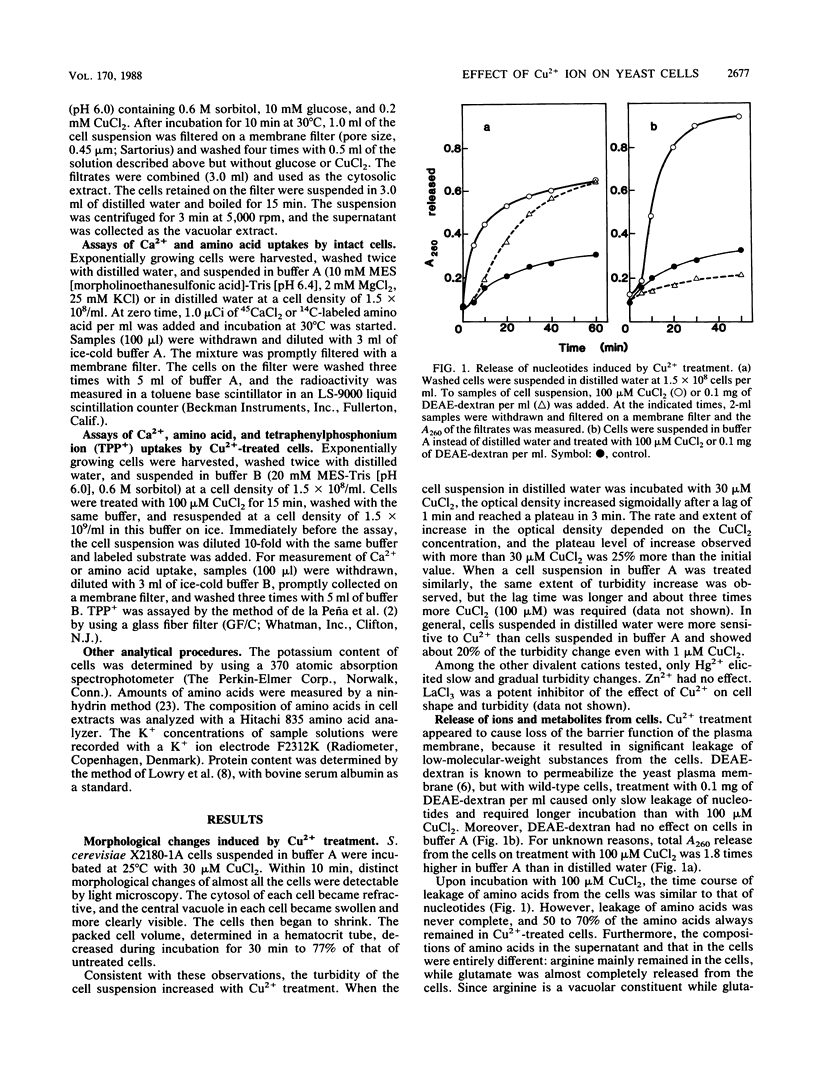
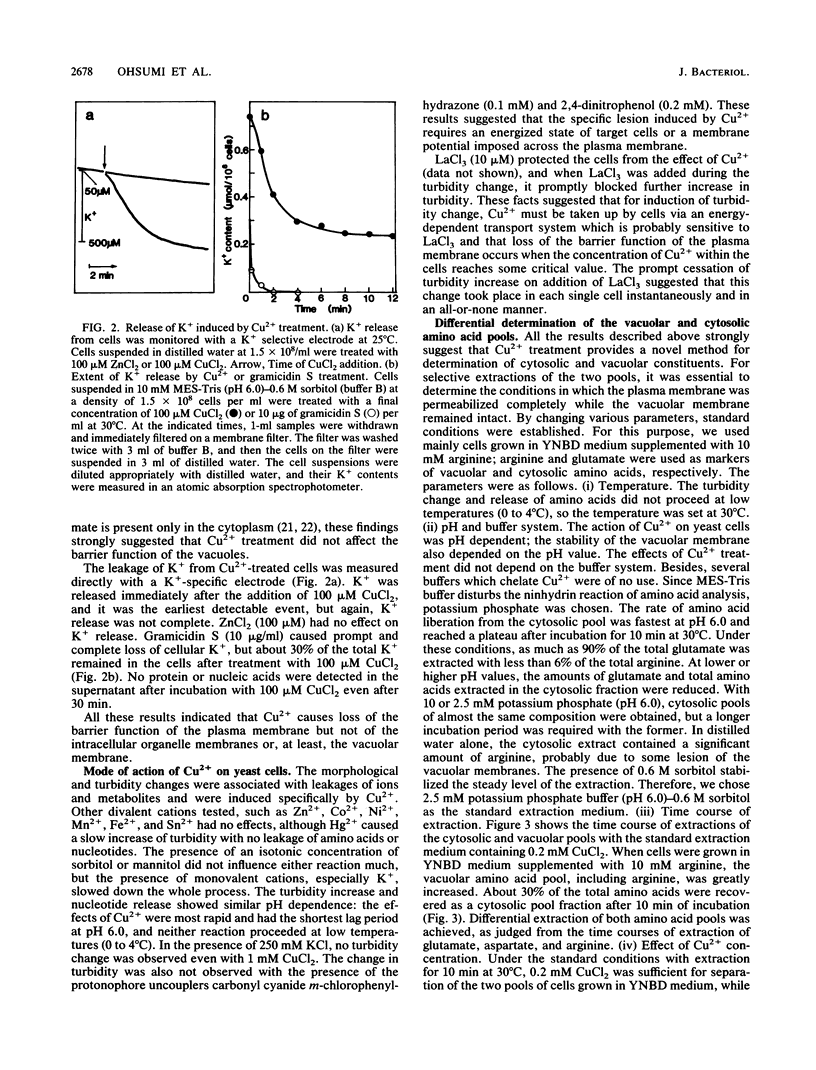
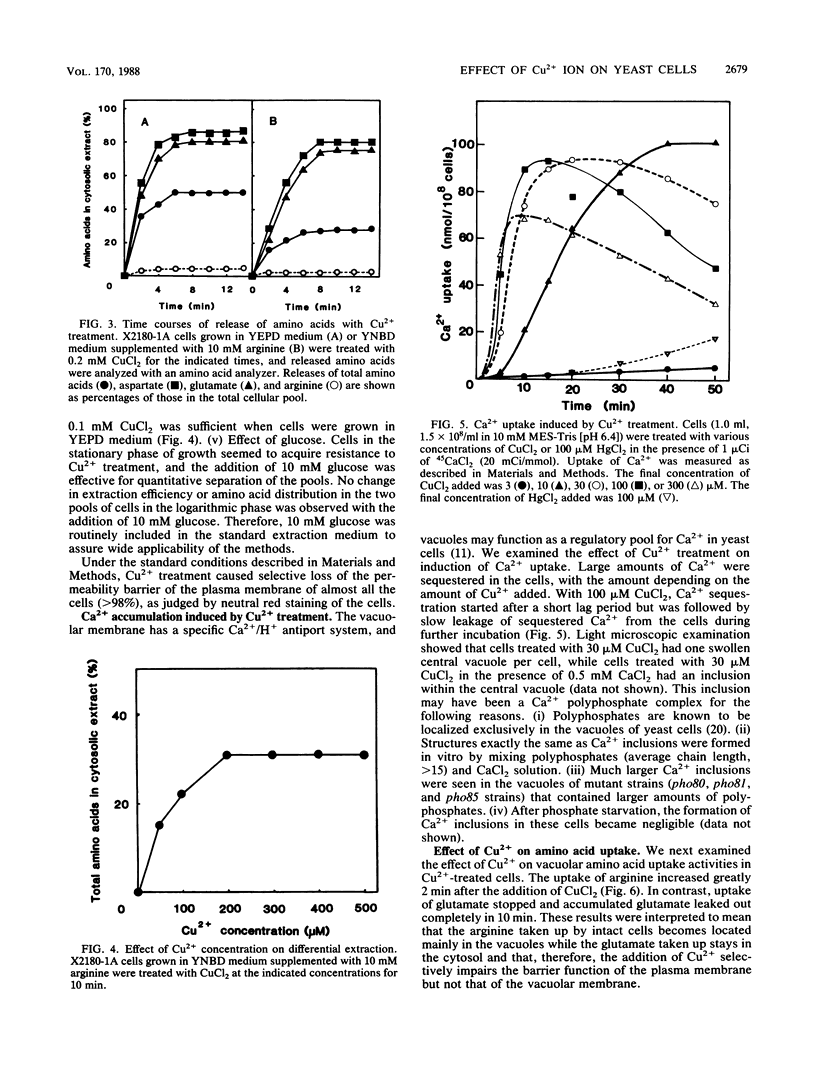
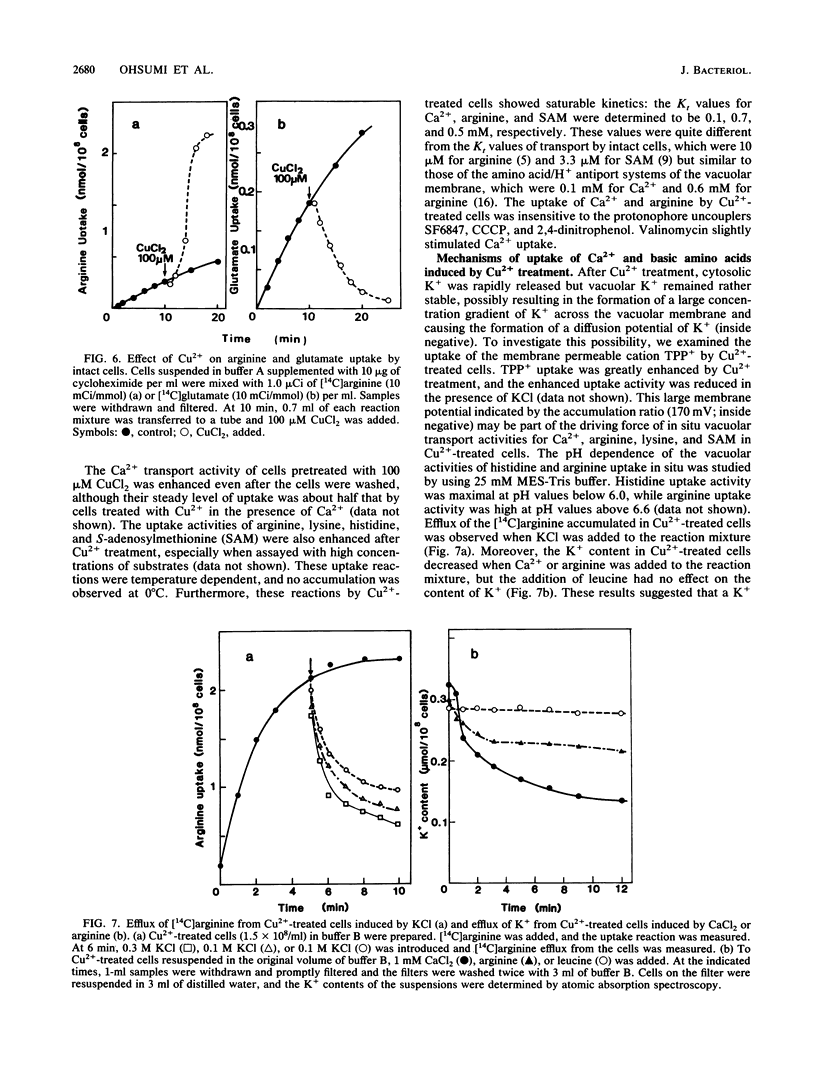
A specific effect of Cu2+ eliciting selective changes in the permeability of intact Saccharomyces cerevisiae cells is described. When 100 microM CuCl2 was added to a cell suspension in a buffer of low ionic strength, the permeability barrier of the plasma membranes of the cells was lost within 2 min at 25 degrees C. The release of amino acids was partial, and the composition of the amino acids released was different from that of those retained in the cells. Mostly glutamate was released, but arginine was mainly retained in the cells. Cellular K+ was released rapidly after CuCl2 addition, but 30% of the total K+ was retained in the cells. These and other observations suggested that Cu2+ caused selective lesions of the permeability barrier of the plasma membrane but did not affect the permeability of the vacuolar membrane. These selective changes were not induced by the other divalent cations tested. A novel and simple method for differential extraction of vacuolar and cytosolic amino acid pools by Cu2+ treatment was established. When Ca2+ was added to Cu2+-treated cells, a large amount of Ca2+ was sequestered into vacuoles, with formation of an inclusion of a Ca2+-polyphosphate complex in the vacuoles. Cu2+-treated cells also showed enhanced uptake of basic amino acids and S-adenosylmethionine. The transport of these substrates showed saturable kinetics with low affinities, reflecting the vacuolar transport process in situ. With Cu2+ treatment, selective leakage of K+ from the cytosolic compartment appears to create a large concentration gradient of K+ across the vacuolar membrane and generates an inside-negative membrane potential, which may provide a driving force of uptake of positively charged substances into vacuoles. Cu2+ treatment provides a useful in situ method for investigating the mechanisms of differential solute pool formation and specific transport phenomena across the vacuolar membrane.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Butt T. R., Sternberg E. J., Gorman J. A., Clark P., Hamer D., Rosenberg M., Crooke S. T. Copper metallothionein of yeast, structure of the gene, and regulation of expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jun;81(11):3332–3336. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.11.3332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fogel S., Welch J. W. Tandem gene amplification mediates copper resistance in yeast. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5342–5346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5342. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grenson M., Mousset M., Wiame J. M., Bechet J. Multiplicity of the amino acid permeases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. I. Evidence for a specific arginine-transporting system. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1966 Oct 31;127(2):325–338. doi: 10.1016/0304-4165(66)90387-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy J. T., Spence K. D. Transport of S-adenosylmethionine in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Bacteriol. 1972 Feb;109(2):499–504. doi: 10.1128/jb.109.2.499-504.1972. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Active transport of basic amino acids driven by a proton motive force in vacuolar membrane vesicles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1981 Mar 10;256(5):2079–2082. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Calcium transport driven by a proton motive force in vacuolar membrane vesicles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1983 May 10;258(9):5614–5617. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okorokov L. A., Lichko L. P., Kulaev I. S. Vacuoles: main compartments of potassium, magnesium, and phosphate ions in Saccharomyces carlsbergenis cells. J Bacteriol. 1980 Nov;144(2):661–665. doi: 10.1128/jb.144.2.661-665.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PASSOW H., ROTHSTEIN A. The binding of mercury by the yeast cell in relation to changes in permeability. J Gen Physiol. 1960 Jan;43:621–633. doi: 10.1085/jgp.43.3.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roomans G. M., Sevéus L. A. Subcellular localization of diffusible ions in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae: quantitative microprobe analysis of thin freeze-dried sections. J Cell Sci. 1976 Jun;21(1):119–127. doi: 10.1242/jcs.21.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. An arginine/histidine exchange transport system in vacuolar-membrane vesicles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11509–11511. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sato T., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Substrate specificities of active transport systems for amino acids in vacuolar-membrane vesicles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Evidence of seven independent proton/amino acid antiport systems. J Biol Chem. 1984 Sep 25;259(18):11505–11508. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwencke J., De Robichon-Szulmajster H. The transport of S-adenosyl-L-methionine in isolated yeast vacuoles and spheroplasts. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 17;65(1):49–60. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10388.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uchida E., Ohsumi Y., Anraku Y. Purification and properties of H+-translocating, Mg2+-adenosine triphosphatase from vacuolar membranes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jan 25;260(2):1090–1095. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Urech K., Dürr M., Boller T., Wiemken A., Schwencke J. Localization of polyphosphate in vacuoles of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 1978 Mar;116(3):275–278. doi: 10.1007/BF00417851. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wada Y., Ohsumi Y., Tanifuji M., Kasai M., Anraku Y. Vacuolar ion channel of the yeast, Saccharomyces cerevisiae. J Biol Chem. 1987 Dec 25;262(36):17260–17263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiemken A., Dürr M. Characterization of amino acid pools in the vacuolar compartment of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Arch Microbiol. 1974;101(1):45–57. doi: 10.1007/BF00455924. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yphantis D. A., Dainko J. L., Schlenk F. Effect of some proteins on the yeast cell membrane. J Bacteriol. 1967 Nov;94(5):1509–1515. doi: 10.1128/jb.94.5.1509-1515.1967. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de la Peña P., Barros F., Gascón S., Ramos S., Lazo P. S. The electrochemical proton gradient of Saccharomyces. The role of potassium. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Apr 1;123(2):447–453. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb19788.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


