Abstract
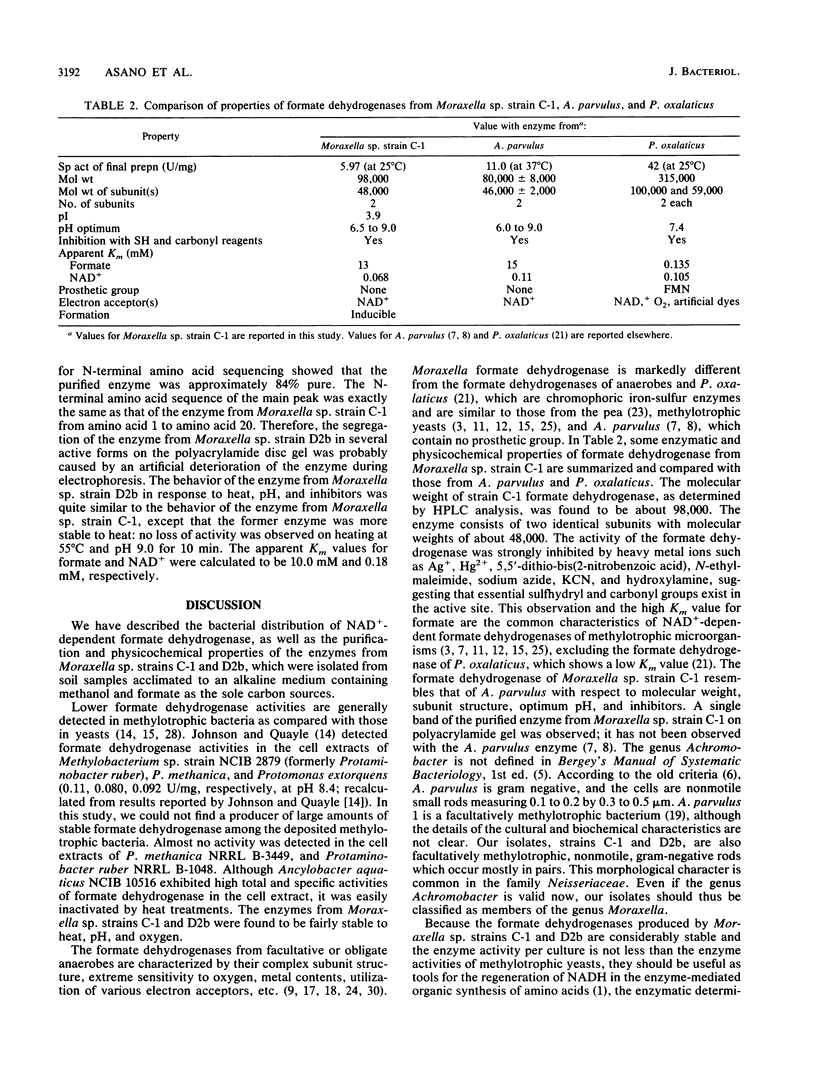
NAD+-dependent formate dehydrogenase was screened in various bacterial strains. Facultative methanol-utilizing bacteria isolated from soil samples, acclimated to a medium containing methanol and formate at pH 9.5, were classified as members of the genus Moraxella. From a crude extract of Moraxella sp. strain C-1, formate dehydrogenase was purified to homogeneity, as judged by disc gel electrophoresis. The enzyme has an isoelectric point of 3.9 and a molecular weight of approximately 98,000. The enzyme is composed of two identical subunits with molecular weights of about 48,000. The apparent Km values for sodium formate and NAD+ were calculated to be 13 mM and 0.068 mM, respectively.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Asano Y., Nakazawa A., Endo K. Novel phenylalanine dehydrogenases from Sporosarcina ureae and Bacillus sphaericus. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jul 25;262(21):10346–10354. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Avilova T. V., Egorova O. A., Ioanesyan L. S., Egorov A. M. Biosynthesis, isolation and properties of NAD-dependent formate dehydrogenase from the yeast Candida methylica. Eur J Biochem. 1985 Nov 4;152(3):657–662. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1985.tb09245.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorov A. M., Avilova T. V., Dikov M. M., Popov V. O., Rodionov Y. V., Berezin I. V. NAD-dependent formate dehydrogenase from methylotrophic bacterium, strain 1. Purification and characterization. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Sep;99(3):569–576. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb13289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Egorov A. M., Tishkov V. I., Avilova T. V., Popov V. O. S-Formyl glutathione as a substrate of bacterial formate dehydrogenase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1982 Jan 15;104(1):1–5. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(82)91932-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enoch H. G., Lester R. L. Formate dehydrogenase from Escherichia coli. Methods Enzymol. 1982;89(Pt 500):537–543. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(82)89093-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ferenci T., Strom T., Quayle J. R. Purification and properties of 3-hexulose phosphate synthase and phospho-3-hexuloisomerase from Methylococcus capsulatus. Biochem J. 1974 Dec;144(3):477–486. doi: 10.1042/bj1440477. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hou C. T., Patel R. N., Laskin A. I., Barnabe N. NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase from methanol-grown Pichia pastoris NRRL-Y-7556. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1982 Jun;216(1):296–305. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(82)90214-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson P. A., Quayle J. R. Microbial growth on C-1 compounds. 6. Oxidation of methanol, formaldehyde and formate by methanol-grown Pseudomonas AM-1. Biochem J. 1964 Nov;93(2):281–290. doi: 10.1042/bj0930281. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kröger A., Winkler E., Innerhofer A., Hackenberg H., Schägger H. The formate dehydrogenase involved in electron transport from formate to fumarate in Vibrio succinogenes. Eur J Biochem. 1979 Mar;94(2):465–475. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1979.tb12914.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liu C. L., Mortenson L. E. Formate dehydrogenase of Clostridium pasteurianum. J Bacteriol. 1984 Jul;159(1):375–380. doi: 10.1128/jb.159.1.375-380.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller U., Willnow P., Ruschig U., Höpner T. Formate dehydrogenase from Pseudomonas oxalaticus. Eur J Biochem. 1978 Feb;83(2):485–498. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1978.tb12115.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- NASH T. The colorimetric estimation of formaldehyde by means of the Hantzsch reaction. Biochem J. 1953 Oct;55(3):416–421. doi: 10.1042/bj0550416. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oyama T., Yamazaki I. Purification and some properties of formate dehydrogenase. J Biochem. 1974 Jun;75(6):1257–1263. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a130509. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- STAFFORD H. A., MAGALDI A., VENNESLAND B. The enzymatic reduction of hydroxypyruvic acid to D-glyceric acid in higher plants. J Biol Chem. 1954 Apr;207(2):621–629. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schauer N. L., Ferry J. G. Composition of the coenzyme F420-dependent formate dehydrogenase from Methanobacterium formicicum. J Bacteriol. 1986 Feb;165(2):405–411. doi: 10.1128/jb.165.2.405-411.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schüte H., Flossdorf J., Sahm H., Kula M. R. Purification and properties of formaldehyde dehydrogenase and formate dehydrogenase from Candida boidinii. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Feb 2;62(1):151–160. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10108.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Triebig G., Schaller K. H. A simple and reliable enzymatic assay for the determination of formic acid in urine. Clin Chim Acta. 1980 Dec 22;108(3):355–360. doi: 10.1016/0009-8981(80)90341-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yagi T. Purification and properties of cytochrome c-553, an electron acceptor for formate dehydrogenase of Desulfovibrio vulgaris, Miyazaki. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Oct 10;548(1):96–105. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(79)90190-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yamamoto I., Saiki T., Liu S. M., Ljungdahl L. G. Purification and properties of NADP-dependent formate dehydrogenase from Clostridium thermoaceticum, a tungsten-selenium-iron protein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):1826–1832. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



