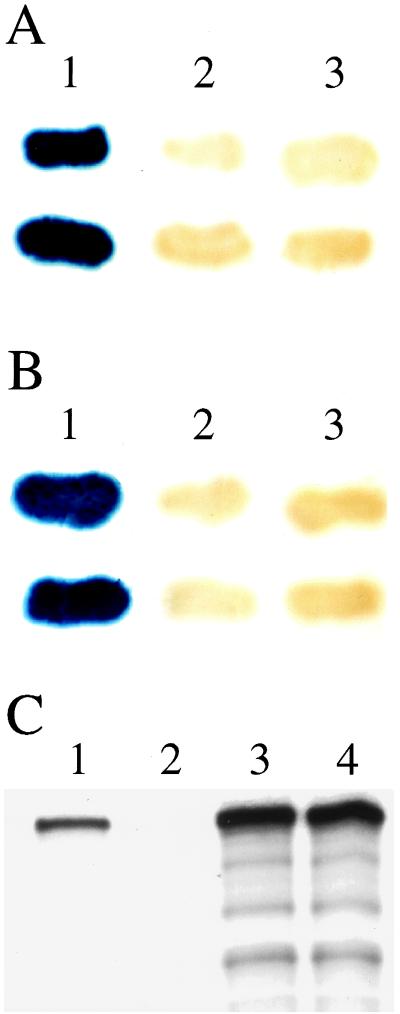
Figure 3.
Yeast two-hybrid and coimmunoprecipitation experiments confirm a physical interaction between the PEX1 and PEX6 proteins. Significant β-galactosidase activity was detected by filter assay of two-hybrid reporter strains coexpressing G4AD–PEX1 and G4BD–PEX6 (A, lane 1) but not in strains coexpressing either G4AD–PEX1 and G4BD (A, lane 2) or G4AD and G4BD–PEX6 (A, lane 3). Significant β-galactosidase activity also was detected in cell lysates of strains coexpressing S. cerevisiae forms of PEX1 and PEX6 (G4AD–ScPEX1 and G4BD–ScPEX6; B, lane 1) but not in strains coexpressing G4AD–ScPEX1 and G4BD (B, lane 2) or G4AD and G4BD–ScPEX6 (B, lane 3). In an independent set of experiments (C), cell free lysates containing [35S]-labeled PEX6 and either unlabeled PEX1–3xmyc or unlabeled PEX1 were subjected to immunoprecipitation with monoclonal anti-myc antibodies. The resulting immunoprecipitates were separated by SDS/PAGE and were assayed by fluorography, revealing significant amounts of [35S]-labeled PEX6 in the immunoprecipitate from the lysate containing PEX1–3xmyc (C, lane 1) but not in the immunoprecipitate from the lysate containing unmodified PEX1 (C, lane 2). Equal amounts of [35S]-labeled PEX6 in these two lysates before immunoprecipitation was confirmed by SDS/PAGE and fluorography (C, lanes 3 and 4, respectively). Control experiments confirmed that PEX1 and PEX1–3xmyc are synthesized equally in vitro and that only PEX1–3xmyc is immunoprecipitated with monoclonal anti-myc antibodies (data not shown).