Figure 3.
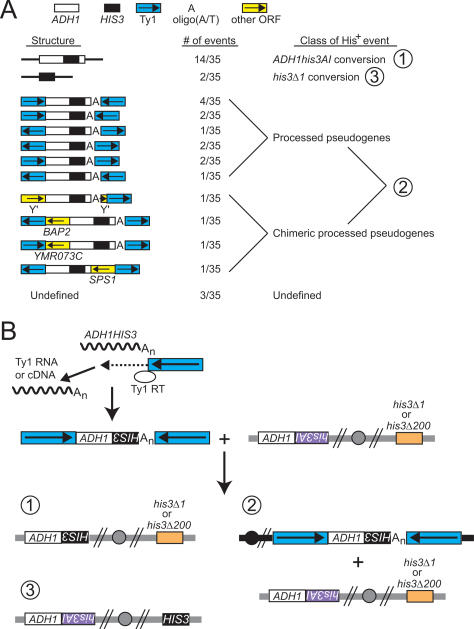
Retrosequences typically replace the donor allele or are flanked by Ty1 sequences. (A) The number of independent His+ events with particular flanking DNA sequences is illustrated. A key at the top indicates which sequences correspond to which symbols, and transcriptional orientations are indicated with arrows. Sequences to the left or right are upstream or downstream relative to ADH1HIS3, respectively. “Undefined” refers to events for which only the upstream or the downstream junction was characterized, and the numbers for different classes correspond to the numbers in B. (B) Ty1 RT is shown using Ty1 cDNA as a primer to initiate reverse transcription of the ADH1HIS3 mRNA starting at the poly(A) tail. At variable points during reverse transcription, Ty1 RT switches templates and begins copying Ty1 RNA or cDNA at sites of microhomology between ADH1HIS3 and Ty1 sequences. One example of the possible junction sites and relative orientations of the retrosequence cDNA and the Ty1 sequences is shown. The botom portion of the diagram is a representation of the recombination events that produced the structures shown in A: ADH1his3AI conversion (1), processed pseudogene formation (2), and his3Δ1 conversion (3). Note that the his3Δ1 allele is present in strains from the BY4742 background, but a complete HIS3 deletion (his3Δ200) is present in strains from the GRF167 background.