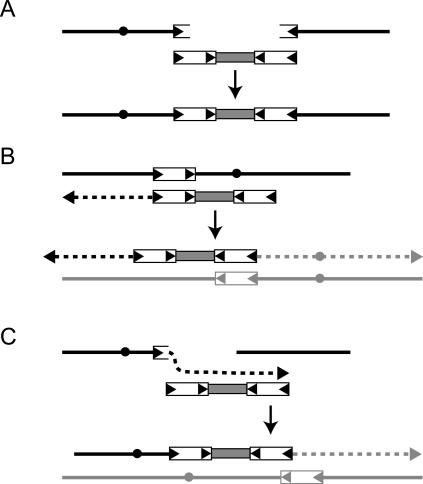
Figure 5.
Models for insertion of retrosequences by SSA or BIR. Black and gray lines represent chromosomes, dotted lines represent newly replicated DNA, white boxes with arrowheads represent Ty1, and gray boxes represent retrosequences. We show only one copy of Ty1 flanking either side of the retrosequence to simplify the drawing, even though our data were consistent with arrays of Ty1 flanking retrosequences at breakpoint junctions. (A) The drawing shows a broken chromosome with breakpoints in Ty1 sequences that is repaired by annealing of Ty1 retrosequence cDNA to each breakpoint. Drawings in B and C show alternative two-step BIR mechanisms for retrosequence insertion that result in nonreciprocal translocations. (B) Each end of Ty1 retrosequence cDNA is extended by separate BIR events that initiate from sites on two different chromosomes (Mieczkowski et al. 2006). (C) A breakpoint on one chromosome is extended by replication of Ty1 retrosequence cDNA, followed by invasion of a second site and replication of the corresponding chromosome fragment.