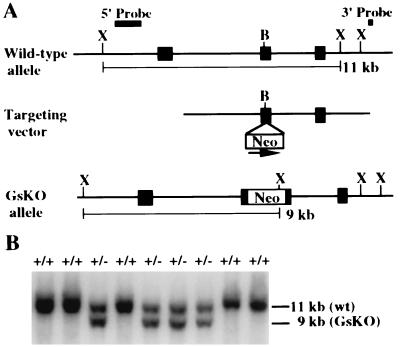
Figure 1.
Generation of Gnas knockout (GsKO) mice. (A) Schematic diagram of the wild type Gnas allele (Top) with exons 1–3 depicted as black boxes. The targeting vector (Middle) was generated by insertion of the GK-Neo cassette into a BamHI (B) site within exon 2 in the same orientation as Gnas (arrow), followed by digestion with SmaI and SstI (the SstI site is contributed by the vector). The recombinant GsKO allele is shown below. The position of the 5′ probe, a NotI-SmaI fragment, is shown above. After digestion with XmnI (X), this probe is predicted to hybridize to an 11-kb genomic fragment in the wild type allele and a 9-kb genomic fragment in the GsKO allele. The position of the 3′ probe used to confirm correct insertion of the targeting vector at the 3′ end is shown above. Southern hybridization using this probe is not shown. (B) Southern hybridization of F1 progeny derived from mating of a GsKO chimera with a CD1 mouse. Genomic DNA was digested with XmnI and hybridized with the 5′ probe. The genotype of individual animals is indicated above each lane.