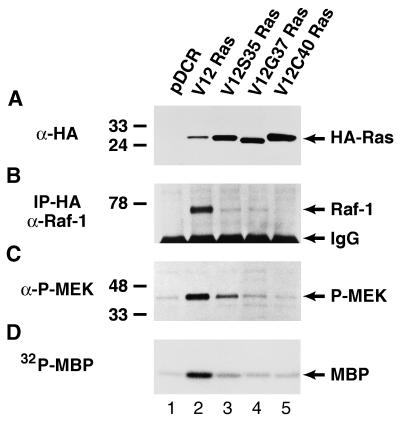
Figure 1.
Characterization of the Ras-Raf-MEK-ERK1/2 pathway in NIH 3T3 (490) cells transfected with vector alone (lane 1), wt V12 Ras (lane 2), V12S35 Ras (lane 3), V12G37 Ras (lane 4) or V12C40 Ras (lane 5). (A) Western blot analysis of HA-tagged Ras oncoproteins showing comparable levels of expression in cell pools stably expressing the different Ras effector domain mutants. The positions of the HA-tagged Ras proteins are shown. (B) Ras-Raf-1 association (coprecipitation) in cells expressing the different Ras effector domain mutants. Cell lysates first were immunoprecipitated with an HA antiserum, followed by anti-Raf-1 Western blotting. The positions of p74Raf-1 and Ig heavy chains are indicated. (C) The levels of MEK phosphorylation (activation) in cells expressing the different Ras effector domain mutants were determined by Western blotting using an antibody against only phosphorylated MEK1/2. Reprobing the blot with an antibody that recognizes total MEK1/2 demonstrated the same level of MEK1/2 expression in all samples (data not shown). The positions of phospho-MEK1/2 are shown. (D) ERK1/2 activity in cells expressing the different Ras effector domain mutants. ERK1/2 immunoprecipitates were used in an in vitro kinase assay with myelin basic protein as a substrate in the presence of {γ-32P}-ATP. The position of phosphorylated myelin basic protein is indicated. The positions of the relative molecular mass markers are shown throughout.