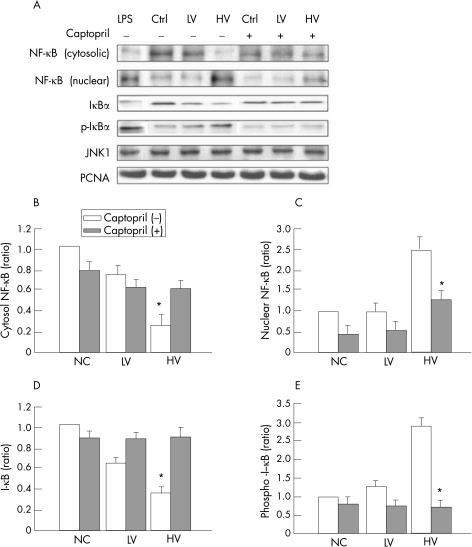
Figure 5 Effect of captopril on the activation of nuclear factor‐κB (NF‐κB) in rat lungs induced by mechanical ventilation. (A) Representative findings of Western blots after 4 h of treatment. (B–E) Relative levels of proteins measured by densitometry of the blots. High‐volume ventilation decreased the cytosol NF‐κB (p<0.001) and I‐κB (p<0.001) levels and increased the nuclear NF‐κB (p = 0.001) and cytosol phosphor‐I‐κB (p<0.001) levels. Captopril pretreatment increased the cytosol NF‐κB (p = 0.01) and I‐κB (p = 0.001) levels and decreased the nuclear NF‐κB (p = 0.005) as well as phosphor‐I‐κB (p<0.001) levels. Ctrl, non‐ventilated control group; JNK1, c‐Jun N‐terminal kinase 1; PCNA, proliferating cell nuclear antigen; NC, normal controls; HV, high‐volume ventilation; LV, low‐volume ventilation.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.