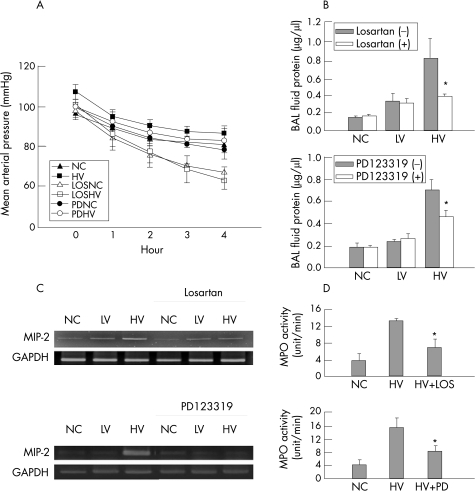
Figure 8 Effects of losartan and PD123319 on ventilator‐induced lung injury. (A) Mean arterial pressures were significantly decreased by losartan (high‐volume (HV) ventilation groups, p<0.001) but not by PD123319 (p = 0.23 between HV groups; n = 6 for each groups). (B) The increase in BAL fluid protein concentration by HV was significantly decreased by losartan (*p = 0.03) and by PD123319 (*p = 0.03; n = 3 for each group). (C) The increase in macrophage inflammatory protein (MIP)‐2 mRNA levels induced by HV was attenuated by losartan and by PD123319. The experiment was repeated three times with similar results. (D) Myeloperoxidase (MPO) assay shows a significant reduction in HV‐induced MPO activity by losartan (*p = 0.004) and by PD123319 (*p = 0.014). LOSHV, high‐volume ventilation with losartan infusion; LOSNC, non‐ventilated control with losartan infusion; PDNC, non‐ventilated control with PD123319 treatment; PDHV, high‐volume ventilation with PD123319 treatment; BAL, bronchoalveolar lavage.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.