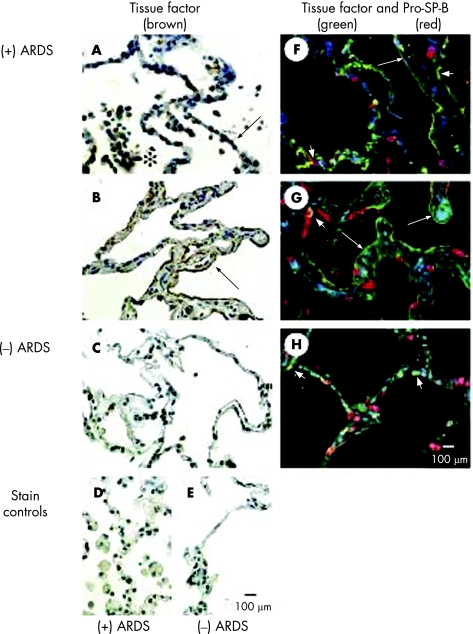
Figure 2 Immunohistochemical localisation of tissue factor (TF) in lung tissue sections from patients who died with acute respiratory distress syndrome ((+) ARDS) or without pulmonary disease ((−) ARDS). (A) Brown reaction product is visible in inflammatory cells (*) in the airspaces and along the epithelial cell lining (arrow) of the airspaces of the lung tissue section from a patient who died with ARDS. Cuboidal alveolar epithelial cells (arrow) are immunostained brown, indicating TF protein localisation. (B) In areas of thickened distal airspace walls of another patient, the squamous alveolar epithelial cells are distinctly immunostained brown (arrow). In contrast, immunolabelling of the occasional inflammatory cells in the airspaces is faint and patchy, and immunolabelling of alveolar epithelial cells is absent in the lung tissue from a patient who died of non‐pulmonary disease (C). Immunostaining controls (omission of the primary antibody) are negative for lung tissue sections from a patient who died with ARDS (D) or with non‐pulmonary disease (E). (F, G) Double immunofluorescence staining was used to identify the cell type of alveolar epithelial cells with TF immunostaining. TF protein was immunolabelled with green fluorochrome and pro‐SP‐B was immunolabelled with red fluorochrome. Squamous alveolar epithelial cells are immunostained green in the tissue sections from the patients who died with ALI/ARDS (large arrows), and cuboidal alveolar epithelial cells are immunostained red (pro‐SP‐B) or yellow (co‐localisation of TF and pro‐SP‐B; short arrows) in the same tissue sections. (H) By comparison, only cuboidal alveolar epithelial cells are immunostained red (pro‐SP‐B) or yellow (co‐localisation of TF and pro‐SP‐B; short arrows) in the tissue section from a patient who died from non‐pulmonary disease. All panels are the same magnification (scale bars in E and H = 100 μm).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.