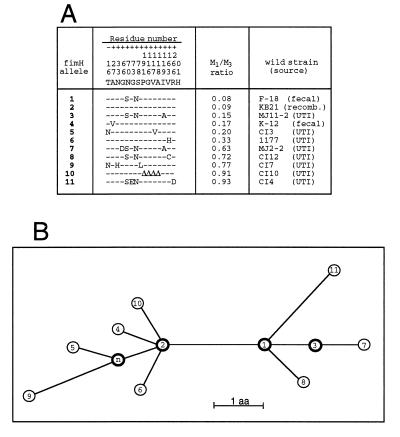
Figure 4.
Phylogenetic analysis of FimH alleles. (A) Amino acid sequences of FimH variants. The alleles are listed based on an increasing M1:M3 binding ratio. The residues listed above the 11 alleles are for the amino acids in original FimH sequence (17) that vary in the other fimH alleles. Only polymorphic residues are shown, and the positions are numbered vertically, from −16 to +201. ▵, deleted residues. (B) Inferred phylogenetic network demonstrating evolutionary relationships of the FimH alleles shown in A. Each node represents a distinct FimH allele, numbered as in A. The allele labeled n represents a hypothetical FimH that differs from allele #2 by the substitution of Asp (N) for Tyr (T) in the leader sequence (residue, −16) and phenotypically should be equivalent to allele #2. Internal nodes are shown in bold. The deduced sequences of the 11 FimH proteins exhibit greater than 99% homology, and the network showing their phylogenetic relationships is fully consistent, without any homoplasty. Branch lengths are scaled to the number of amino acids that differ between alleles, as indicated. The deletion of 4 amino acids in FimH allele #10 is considered to be a single event, equivalent to one amino acid substitution.