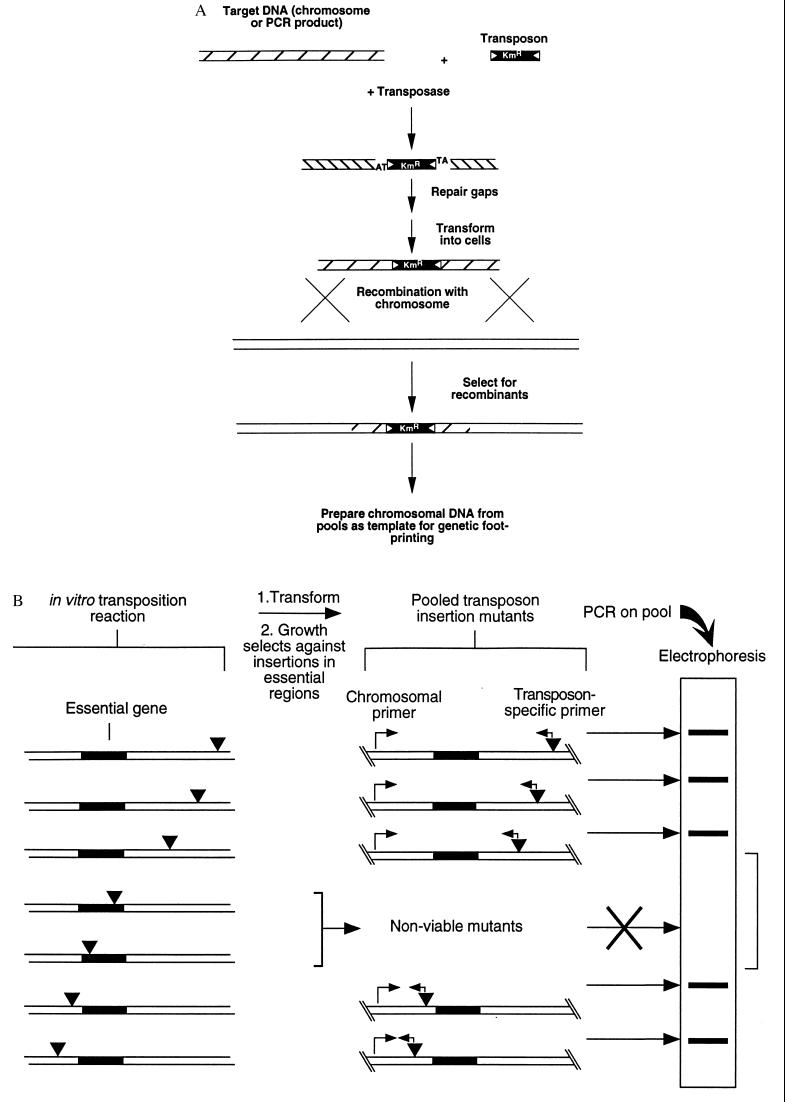
Figure 1.
Schematic diagram of the two steps required for GAMBIT (a) Strategy for producing chromosomal mutations by using in vitro transposon mutagenesis. (b) Genetic footprinting for detection of essential genes. Target DNA mutagenized in vitro with the Himar1 transposon was introduced into bacteria by transformation and homologous recombination. Recombinants were selected for drug resistance encoded by the transposon, and insertions in essential genes were lost from the pool during growth. PCR with primers that hybridize to the transposon and to specific chromosomal sites yielded a product corresponding to each mutation in the pool. DNA regions containing no insertions yielded a blank region on electrophoresis gels.