Figure 5.
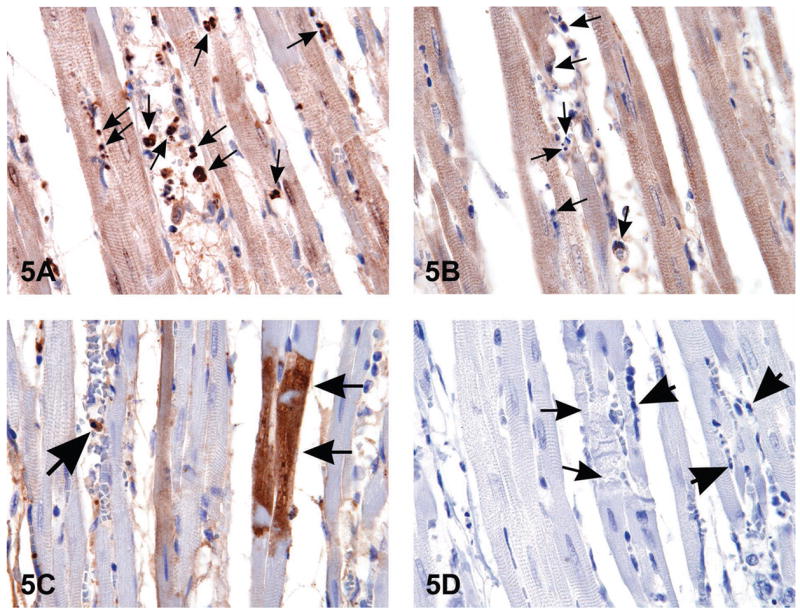
When histological changes suggestive of apoptosis are detected in H&E stained tissues (i.e., Figure 1B), confirmation of apoptosis can be obtained with a variety of additional stains. The images in Figure 5 are of myocardium from 14-week-old rats treated with ephedrine (25 mg/kg) and caffeine (30 mg/kg). Figure 5A is the interventricular septum stained by anti-phospho-H2A.X, a histone variant that becomes phosphorylated during apoptosis; note the strongly stained apoptotic bodies (arrows). Figure 5B demonstrates the negative control of the same section shown in (A); nonimmune rabbit IgG was used at equivalent conditions in place of the primary antibody. Note the unstained apoptotic bodies (arrows). Figure 5C illustrates cleaved caspase-3 staining for apoptosis revealing the presence of intracytoplasmic positive myofibers (small arrows) located in the interventricular septum; large arrow indicates an apoptotic body. Figure 5D is a negative control of the same heart demonstrated in 5C. The small arrows demonstrate degenerating myofibers; large arrows indicate apoptotic bodies. Nyska et al., 2005, by permission 2 of Oxford University Press.
