Figure 2.
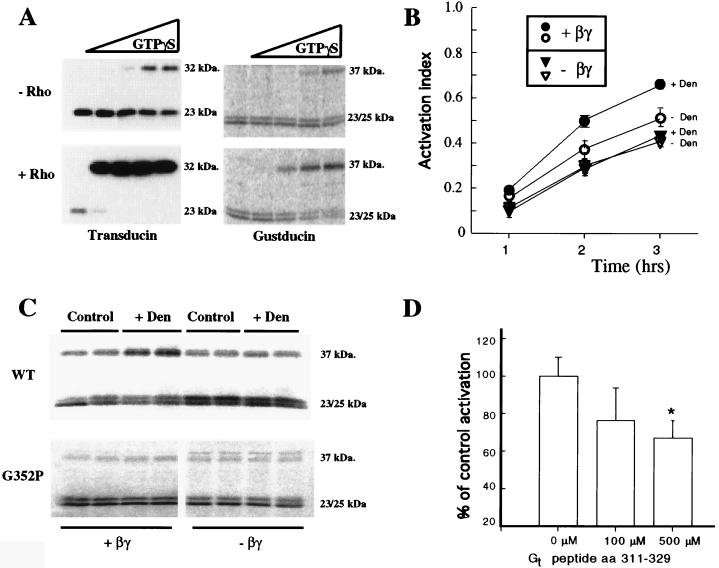
Gustducin is activated by a presumptive heptahelical taste receptor. (A) Rhodopsin activation of transducin and gustducin was assessed by the trypsin cleavage pattern (“trypsin assay”). The nonactivated (GDP-bound) forms of native transducin (Left), or in vitro translated gustducin (Right) generate 23- and 23- plus 25-kDa tryptic fragments, respectively. The active (GTP[γS]-bound) conformations of the G-proteins generate 32-kDa (transducin) or 37-kDa (gustducin) fragments. Increasing concentrations of GTP[γS] (0.1, 1, 10, and 100 μM for transducin; 0.001, 0.1, 1, and 10 μM for gustducin) caused rhodopsin-independent activation of the G-proteins, but only at the highest GTP[γS] concentrations. Rhodopsin (Lower) enhanced this activation by ≈100- to 1000-fold. +Rho, 1 μM rhodopsin. (B) Activation of gustducin by denatonium-stimulated taste membranes required G-protein βγ subunits. In the absence of βγ subunits (-βγ, triangles) there was only a slight elevation, with increasing time of incubation, in the activation index (the ratio of the 37-kDa form diagnostic of activation versus the sum of the intensities of the 37- plus 23/25-kDa bands) of gustducin in the presence of taste membranes with or without the bitter tastant denatonium. When βγ subunits were added (+βγ, circles), denatonium-stimulated taste membranes increased the activation of gustducin by greater than 2-fold. Each point is the average of four independent quantitations of duplicate samples. Error bars represent the standard deviation. The displayed results are representative of three independent experiments. +Den (filled symbols), 2.5 mM denatonium. (C) Trypsin assays to monitor gustducin/transducin activation. Upper, Wild-type (WT) in vitro translated gustducin was activated by denatonium-stimulated taste membranes when βγ subunits were added (+βγ, Left) but not in their absence (-βγ, Right). Lower, G352P gustducin, a mutant defective in its interaction with rhodopsin, was not activated by taste membranes in the presence (+βγ, Left) or absence (-βγ, Right) of βγ subunits. Representative gels containing duplicate independent samples are shown. +Den, 2.5 mM denatonium. Control, water added in place of denatonium. (D) The Gt peptide, corresponding to amino acids 311–329 of transducin (one of transducin’s primary sites of interaction with rhodopsin), inhibited by ≈50% the denatonium-dependent taste membrane activation of in vitro translated gustducin. The results shown are the average of six independent experiments with duplicate samples. ∗, P < 0.05, Student’s t test.