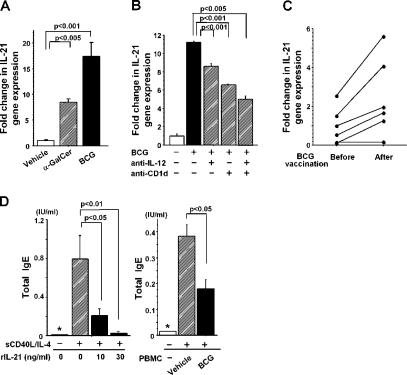
Figure 6.
IL-21 mRNA expression and IL-21–induced IgE suppression in humans. (A) IL-21 mRNA expression in PBMCs. 106 human PBMCs were stimulated with 100 ng/ml α-GalCer or 50 μg/ml BCG and examined for IL-21 expression by quantitative real-time PCR with Taqman probes. The data are representative of five donors. (B) IL-12 and CD1d are required for IL-21 expression. 106 PBMCs were stimulated in vitro with 50 μg/ml BCG in the presence of 10 μg/ml anti-CD1d and/or anti–IL-12p40/p70 mAb. Representative data from five donors are shown. (C) IL-21 mRNA expression in PBMCs. Healthy volunteers were inoculated intradermally with BCG (two drops of 26.7 mg/ml of BCG emulsion per person). In A–C, the data for IL-21 expression were normalized to 18S ribosomal RNA expression, and relative expression levels are shown. Statistical analysis was performed using a matched pairs t test in C. (D) Suppression of IgE production. Left, suppression of IgE production by IL-21. 2 × 105 human B cells were cultured with sCD40L and IL-4 in the presence of human IL-21 for 14 d. Right, suppression of IgE production by BCG-activated human PBMCs. 105 Bɛ cells were cocultured with 105 PBMCs, sCD40L, and IL-4 in the presence of 50 μg/ml BCG for 14 d. Total IgE was measured by ELISA. Values are expressed as mean ± SD of triplicate cultures. The asterisks (*) indicate that the IgE levels are below the detection limit for total IgE (<0.014 IU/ml). Data shown are representative of three donors. Results were expressed as a fold difference in human IL-21 gene expression relative to a control sample (vehicle) after being normalized with 18S ribosomal RNA expressions in each sample.