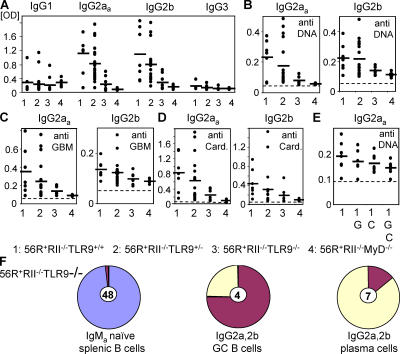
Figure 5.
The TLR9 pathway was required for generation of IgG2a and 2b anti-DNA/polyreactive autoantibodies. IgG subclass analysis of autoantibodies in the serum of 7–11-wk-old 56R+RIIB−/−TLR9+/+.B6 (n = 7), 56R+RIIB−/−TLR9+/−.B6 (n = 19), 56R+RIIB−/−TLR9−/−.B6 (n = 7), or 56R+RIIB−/−MyD88−/−.B6 (n = 6) mice as determined by ANA (A), anti-DNA (B), antiglomerular basement membrane (anti-GBM) (C), and anticardiolipin (D) ELISA, indicated a reduction of the autoreactive IgG2aa and IgG2b subclasses for both genotypes (P = 0.007 and P = 0.03, respectively, for the ANA ELISA). (E) Polyreactivity was analyzed by preabsorbing the samples on the indicated ELISA plates; G: GBM; C: cardiolipin; G,C: GBM + cardiolipin. (F) TLR9-deficient IgMa + naive splenic B cells retained the intact 56R VDJ4H transgene, whereas IgG2a and 2b positive TLR9-deficient GC and splenic plasma cells did not use the intact 56R VDJ4H transgene (compare with Fig. 3).