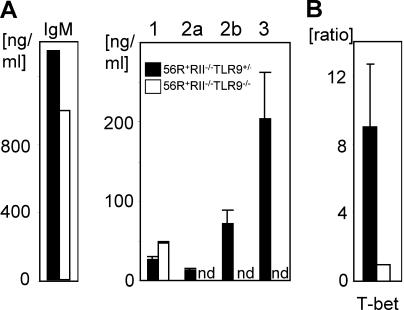
Figure 6.
Loss of IgG2a and 2b autoantibodies in TLR9-deficient mice was B cell autonomous. (A) Naive splenic B cells from the indicated genotypes were stimulated with 15 μg/ml CpG1826, 10 μg/ml anti-CD40, and 10 ng/ml rmIL-4 in vitro for 5 d and total Ig subclass concentrations in the supernatants were determined. Class switching to IgM was unchanged and to IgG1 increased in TLR9-deficient backgrounds. In contrast, switching to IgG2a, 2b, and 3 was significantly impaired. (B) T-bet mRNA is not induced by CpG stimulation of B cells in the TLR9-deficient background. A portion of the cells in (A) were collected after 12 h of the indicated stimulation. mRNA and cDNA were prepared and used for real-time PCR with specific primers for T-bet and β-actin as an internal control. The ratio between TLR9-sufficient and -deficient B cells for T-bet mRNA was calculated after normalizing for β-actin. nd, not detected. Results from three independent experiments are shown as mean ± SD.