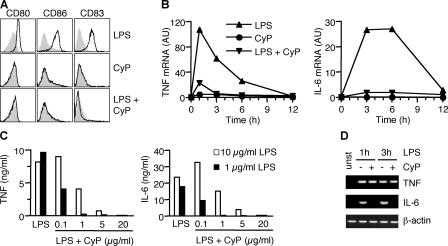
Figure 1.
CyP inhibits LPS-induced activation of human DCs in a dose-dependent manner. (A) Human monocyte-derived DCs were treated with 1 μg/ml LPS and 20 μg/ml CyP alone or in combinations. After 16 h, expression of CD80, CD86, and CD83 was measured. Untreated DCs are shown in each panel as a gray profile. One representative experiment of six is shown. (B) Kinetics of TNF and IL-6 mRNA expression in DCs treated with LPS (▴), CyP (•), or LPS and CyP (▾) as measured by quantitative real-time RT-PCR. One representative experiment of five is shown. Fig. S2 shows additional transcript analysis. (C) DCs were stimulated with 10 (white bars) or 1 (black bars) μg/ml LPS in the absence or presence of graded amounts of CyP. After 20 h, TNF and IL-6 were measured in the culture supernatants by ELISA. One representative experiment of three is shown. (D) Nascent mRNA was isolated from the nuclei of DCs before (unst) and 1 or 3 h after stimulation by LPS in the absence (−) or presence (+) of CyP, and PCR was performed using specific primers.