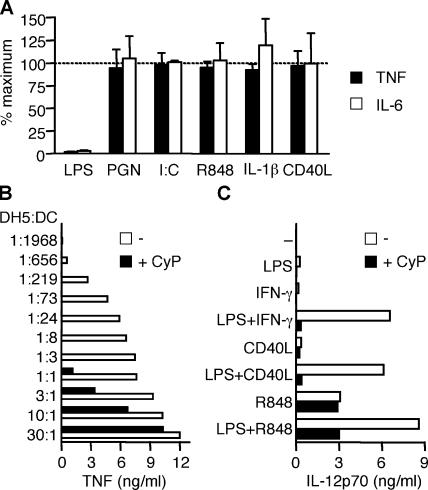
Figure 2.
CyP specifically inhibits LPS stimulation of DCs. (A) DCs were stimulated for 16 h with different TLR agonists (1 μg/ml LPS, 10 μg/ml PGN, 20 μg/ml poly(I:C), and 2.5 μg/ml R848), 20 ng/ml IL-1β, or 1 μg/ml soluble CD40L in the absence or presence of 20 μg/ml CyP. Data are expressed as the percentage of the response (TNF production, black bars; IL-6 production, white bars) obtained with the specific agonists in the absence of CyP and represent the mean ± SD of four independent experiments. Inhibition of LPS was found to be statistically significant (P < 0.0001), whereas inhibition of all other stimuli was found to be nonsignificant (P > 0.05). (B) DCs were challenged with graded numbers of DH5α bacteria in the absence (white bars) or presence (black bars) of 20 μg/ml CyP. TNF was measured in the 20-h culture supernatants by ELISA. CyP did not affect bacterial growth. One representative experiment of three is shown. (C) DCs were stimulated with LPS, 10 ng/ml IFN-γ, soluble CD40L, or R848 alone or in the indicated combinations in the absence (white bars) or presence (black bars) of CyP. IL-12p70 was measured in the 24-h culture supernatants. One representative experiment of four is shown.