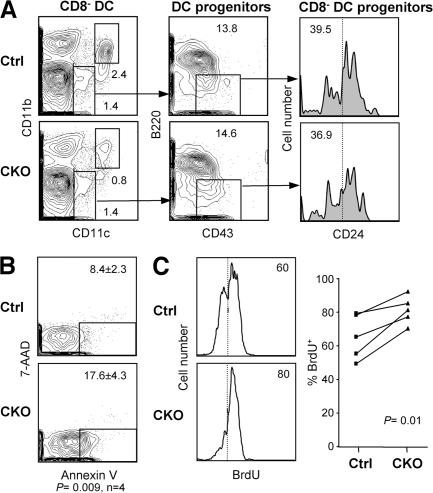
Figure 5.
Impaired survival and homeostasis of RBP-J–deficient splenic CD8− DCs. (A) Splenic DC progenitors, including CD24low DC progenitors committed to the CD8− subset, in control (RBP-Jfl/fl) and CKO (RBP-Jfl/fl CD11c-Cre+) mice. The fraction of each subset in the gated population (mean of two animals) is indicated. The fraction of CD24−/low cells corresponding to CD8− DC progenitors is indicated by the vertical dotted line. (B) The expression of the apoptotic marker phosphatidylserine in control and CKO CD8− DCs, as determined by Annexin V staining. Shown are the representative profiles of ex vivo–isolated CD8− DCs stained with Annexin V and the dead-cell marker 7-amino-actinomycin D, with the fraction of apoptotic cells indicated (mean ± SD of four mice). (C) The turnover rate of splenic CD8− DCs. Mice were fed BrdU for 4–5 d, and the fraction of BrdU+ CD8− DCs (dotted line) was determined by flow cytometry. Shown are the representative BrdU staining profiles of gated CD8− DCs and the fraction of BrdU+ CD8− DCs in control and CKO mice. Because the efficiency of BrdU incorporation and staining varied between experiments, control and CKO mice from each experiment were compared pairwise and analyzed using the paired Student's t test.