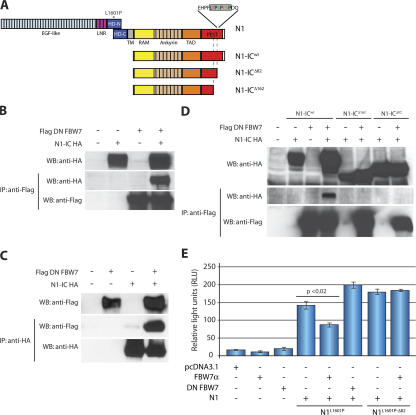
Figure 1.
Physical and functional association between FBW7 and NOTCH1. (A) Schematic depiction of the NOTCH1 (N1) protein domains, and N1-IC WT (N1-ICWT) and 82 and 162 ΔPEST mutants (N1-ICΔ82 and N1-ICΔ162). Asterisk denotes L1601P mutation. The FBW7 degron is highlighted in gray. LNR, LIN-Notch repeat domain; RAM, RBJ-κ–associated module; TAD, transcriptional activation domain; PEST, P-E-S-T–rich domain; HD, heterodimerization domain. (B and C) Coimmunoprecipitation experiments using anti-Flag beads or anti-HA beads, showing interaction between DN FBW7 and N1-ICWT, but DN FBW7 (D) does not interact with N1-ICΔ82 and N1-ICΔ162. (E) Cotransfection with FBW7α repressed N1L1601P (P < 0.02), but not N1L1601P-Δ82, in reporter assays using a CSL luciferase reporter. pCDNA3.1 represents the control, “empty” expression vector. Error bars represent the SD of duplicate wells.