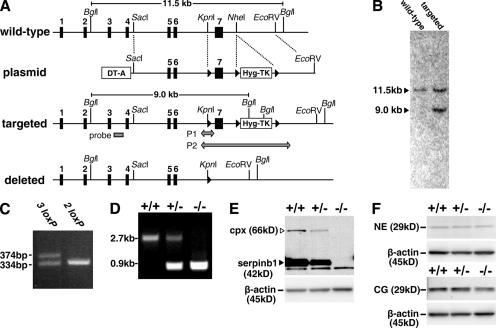
Figure 1.
Generation of serpinb1−/− mice. (A) The WT serpinb1 gene locus comprises seven exons (black rectangles). The targeting plasmid featured a negative selection cassette (DT-A) and a positive/negative selection cassette (Hyg-TK) flanked by two loxP sites (black triangles). The long homology arm also included a third loxP site in intron 6. Targeted ES clones selected for hygromycin resistance but not expressing DT-A were selected for homologous recombination by Southern blotting using an external probe in intron 3 (gray rectangle) after Bgl I restriction. Selected clones were further tested by PCR for the presence of the third loxP site in intron 6 (P1 arrow). ES clones with the deleted locus were identified by PCR (P2 arrow) after transient Cre expression and gancyclovir selection of targeted ES clones. (B) Southern blot of ES clones with WT or targeted loci. (C) PCR P1 was used to select homo logous recombination ES clones that contained the loxP site in intron 6 (denoted as 3 loxP). (D) PCR P2 of mouse tail genomic DNA was used to genotype WT (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous (−/−) deleted serpinb1 mice. (E and F) Analysis of bone-marrow neutrophils. (E) Western blot analysis shows the native 42-kD serpinb1 (arrowhead) and the 66-kD serpinb1 complexed with neutrophil proteases (cpx). Protein molecular mass markers are indicated. Lower molecular mass nonspecific bands are also visible. (F) Western blot analysis show 29-kD NE (top) and CG (bottom). Blots were restained for β-actin to indicate equal protein loading.