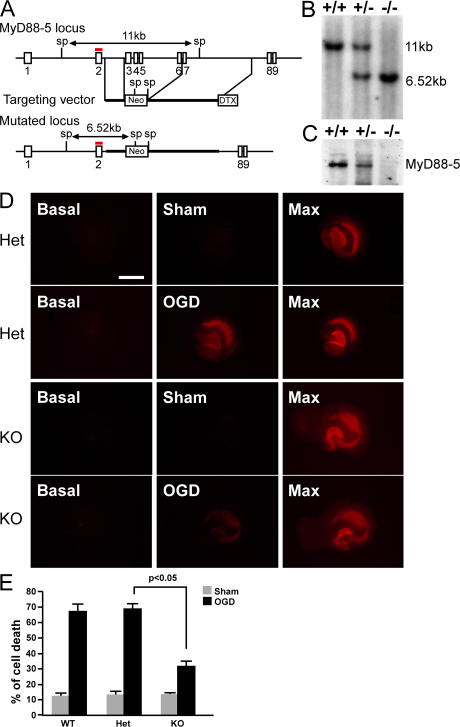
Figure 5.
Generation of MyD88-5 knockout mice and protection of their hippocampal neurons from OGD-induced cell death. (A) Schematic of the MyD88-5 locus, targeting vector, and predicted structure of the mutated locus. Exon numbers are indicated. The probe used for Southern blotting is shown in red. Restriction enzyme sites and predicted sizes of the digests are shown. Sp, SphI; Neo, neomycin resistance gene; DTX, diphtheria toxin gene. (B) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA from MyD88-5 wild-type, hemizygous-deficient, and null mice. (C) Western blot analysis of MyD88-5 expression in wild-type, hemizygous-deficient, and null mice. 50 μg of brain lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE. Affinity-purified chicken anti–MyD88-5 antibody was used for detection. (D) Propidium iodide staining of dead neurons in hippocampal slices at the start of the OGD period (basal), after OGD (OGD), or the same period without OGD treatment (sham), and after exposure to 1 mM NMDA to induce a maximal cell death (Max). Hippocampi illustrated were from MyD88-5+/− (Het) or MyD88-5−/− mice (KO). Bar, 1 mm. (E) Quantitative evaluation of cell death after sham or OGD treatment in MyD88-5+/+ (sham, n = 6; OGD, n = 13) MyD88-5+/− (sham, n = 11; OGD, n = 22) and MyD88-5−/− (sham, n = 5; OGD, n = 29) slices. P < 0.05, Student's t test.