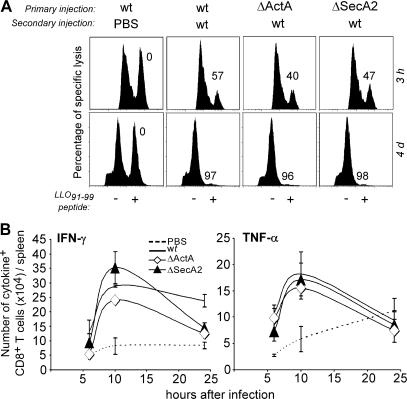
Figure 3.
Cytolytic and IFN-γ–/TNF-α–secreting activities of CD8+ T cells in mice primary immunized with WT and mutants of L. monocytogenes. BALB/c mice (five per group) primarily immunized with PBS or 0.1 × LD50 of the indicated bacteria (PBS, secA2 −, actA −, or WT) were secondary challenged 30 d later with either PBS, 3 × 105, or 104 (A, bottom) WT bacteria. (A) 3 h (top) or 4 d (bottom) after secondary challenge, animals were transferred with 107 CFSElow unpulsed and CFSEhigh LLO91-99 peptide–pulsed target cells. Spleen cells from individual mice were analyzed by FACS 15 h later. Data show representative FACS histograms in one out of three experiments. The numbers indicate the percentage of specific lysis of peptide-pulsed CFSEhigh cells. (B) At specified times, spleen cells from individual mice (three per group) were restimulated in vitro with LLO91-99 and analyzed by FACS for intracellular staining of IFN-γ and TNF-α. Data show the total numbers (mean ± SE) of IFN-γ– (left) and TNF-α– (right) secreting CD8+CD3+ T cells per spleen in a representative (out of three) experiment.