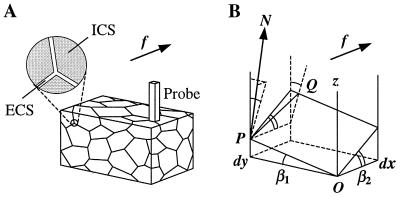
Figure 1.
Diagram illustrating derivation of the elementary geometric tortuosity of a porous medium. (A) A schematic diagram of a porous medium fragment with a thin and narrow rectangular prism probe situated perpendicular to the direction of diffusion f. The expanded section shows the relationship of extracellular and intracellular spaces (ECS and ICS, respectively). (B) Geometry of the infinitesimal approximation: the thin and narrow probe cuts a parallelogram K out of the extracellular space (between two cell surfaces); a diffusing particle encounters the probe at point P and then travels on surface K along path dq = PQ; the spatial position of K is determined by angles β1 and β2 (shown).