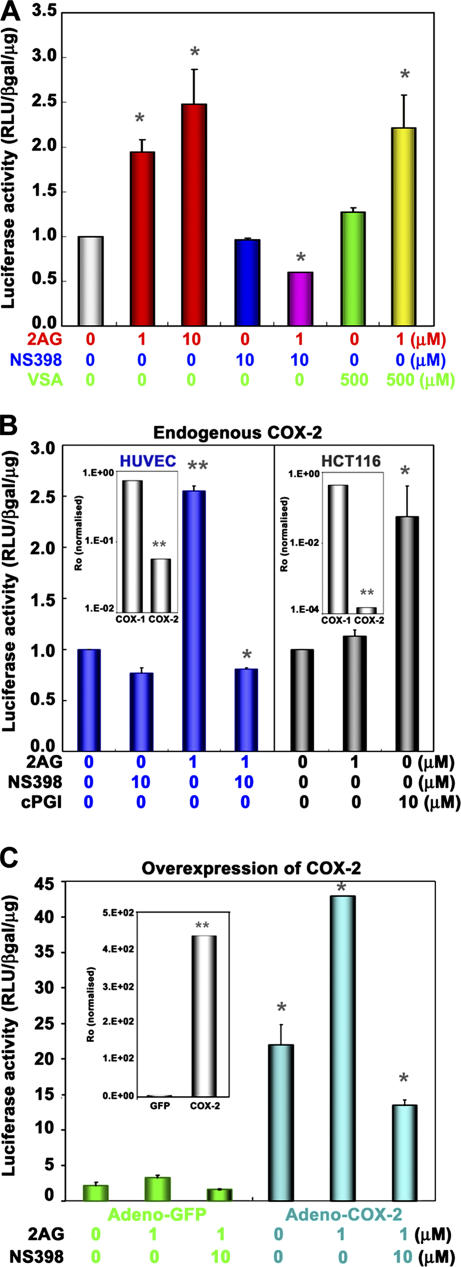
Figure 2.
COX–2 activity is required for endocannabinoid-induced PPARδ transcription. (A) HUVECs were transiently transfected with pACO-gLuc as described in Fig. 1. Cells were pretreated with a COX-2–selective inhibitor (NS398; 10 μM) or a COX-1–selective inhibitor (VSA; 500 μM) for 30 min, followed by the addition of 2-AG or DMSO (vehicle) for 16 h (*, P < 0.05, compared with vehicle). (B) Transactivation of the PPRE reporter plasmid in HUVECs (blue), but not in HCT116 (gray), which is a COX-2–null cell line. (B, insets) mRNA levels of COX-1 and -2 in these cells by qRT-PCR (*, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01, compared with vehicle). (C) Overexpression of COX-2 enhances 2-AG–induced PPARδ transactivation. HUVECs were transduced with either adeno-GFP (green) or adeno–COX-2 virus (blue) treated with 1 μM 2-AG as in Fig. 1, with or without 10 μM NS-398, and PPARδ transcriptional activity was assayed as in Fig. 1. (C, inset) COX-2 mRNA expression (**, P < 0.01, compared with control vector virus, inset *, P < 0.05; compared with vehicle).