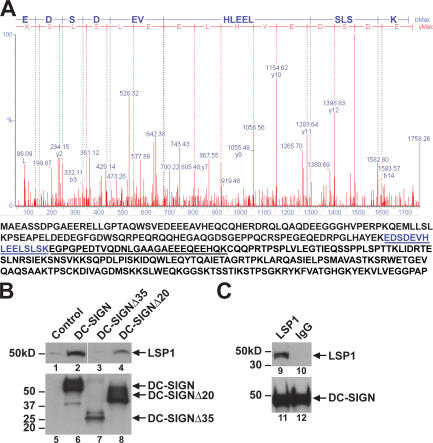
Figure 3.
LSP1 associates with the cytoplasmic domain of DC-SIGN. (A) Identification of proteins interacting with the cytoplasmic domain of DC-SIGN. Raji cells, expressing DC-SIGN, DC-SIGNΔ35, and DC-SIGNΔ20 were lysed in cell lysis buffer and 2 mg of total protein was incubated overnight with 5 μg of monoclonal anti–DC-SIGN antibody and protein G conjugated to agarose beads at 4°C. The immunoprecipitated material was washed and suspended in 2-D gel electrophoresis loading buffer. After 2-D gel electrophoresis, gels were stained with Coomassie blue. Coomassie-stained protein spots that were unique for the full-length DC-SIGN were picked, digested with trypsin, and analyzed by MALDI-TOF. A representation of the mass spectrometry data for the 15–amino acid LSP1 peptide is shown (top). Protein sequence of LSP1 is shown, and the peptides identified by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight are underlined (bottom). (B) LSP1 interacts with full-length DC-SIGN but not the cytoplasmic tail–deleted mutant. The parental cell line Raji-1 and Raji B cells expressing DC-SIGN and nonfunctional mutants DC-SIGNΔ35 and DC-SIGNΔ20 were lysed, and total protein was immunoprecipitated with monoclonal anti–DC-SIGN antibody and protein G conjugated to agarose beads overnight at 4°C. Immunoprecipitates were assayed for LSP1 (lanes 1–4) and DC-SIGN (lanes 5–8) expression using polyclonal antibodies by immunoblot. The control represents cell lysate from the parental cell line Raji-1. (C) LSP1 interacts with DC-SIGN in human DCs. Human MDDCs were isolated from healthy donors and cultured in RPMI, 50 ng/ml hGM-CSF, and 100 ng/ml IL-4 for 7 d before being lysed, and total protein was immunoprecipitated in the presence of protease inhibitors with a monoclonal anti–DC-SIGN antibody conjugated to agarose beads. Immunoprecipitates were assayed for LSP1 (lanes 9 and 10) and DC-SIGN (lanes 11 and 12) expression using polyclonal antibodies by immunoblot.