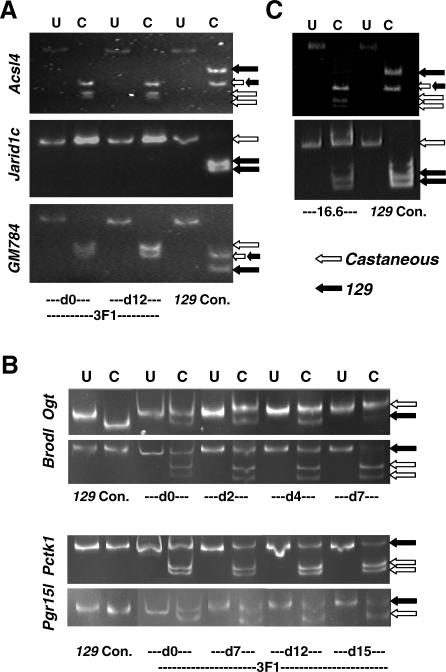
Figure 6. Allele-Specific Analysis of X-Linked Gene Expression during Differentiation of Hybrid (129 × castaneous) Female ES Cells.
(A) Electrophoretic separation of cDNA restriction fragments from the three cluster 4 genes Acsl4, Jarid1c, and GM784 reveals allele-specific expression. PCR fragments that are specific for each gene were prepared from cDNAs from undifferentiated (day 0) or differentiated (day 12) 3F1 hybrid ES cells. Fragments were uncut (U) or cut (C) with restriction enzymes, so as to reveal SNPs that distinguish m.m.domesticus (129, black arrows) and m.m.castaneous (white arrows) alleles. Small double arrows show where bands of the same size are generated from 129 and castaneous. For all three genes, the expected 129 product is missing from both undifferentiated (day 0) and differentiated (day 12) cells, showing that expression is exclusively from the castaneous allele. cDNA from the male CCE/R ES cell line provided the 129 control. Details of primers, restriction enzymes, and expected fragment sizes are given in Table S5.
(B) Electrophoretic separation of cDNA restriction fragments from four X-linked genes Ogt, Brodl, Pctk1, and Pgr15l to reveal allele-specific expression in 3F1 hybrid female ES cells at different days of differentiation (days 0–15 as indicated); labelling as for (A).
(C) In undifferentiated 16.6 hybrid female ES cells, cluster 4 gene Acsl4 (upper gel) shows monoallelic expression (castaneous allele only) while Jarid1c (lower gel) is expressed from both alleles; labelling as for (A).