Figure 1.
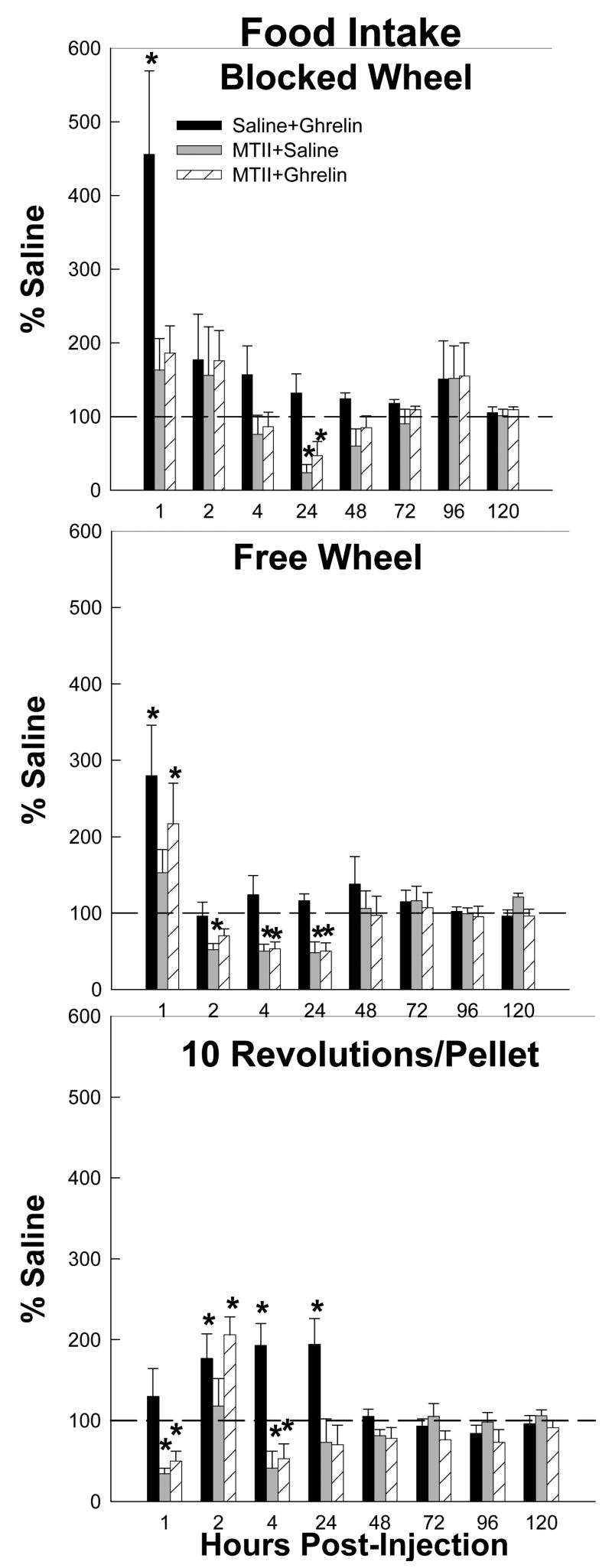
Mean ± SEM of food intake as a percentage of the intracerebroventricularly (icv) and intraperitoneally (ip) saline-injected controls (dashed reference line) for the effects of ip ghrelin treatment with icv saline (black bars), ip saline treatment with icv melanotan II (MTII; gray bars) and ip ghrelin treatment with icv MTII (striped bars) on hamsters without a foraging requirement and a stationary wheel (Blocked Wheel), hamsters with no foraging requirement and a freely moving wheel (Free Wheel) and hamsters with a foraging requirements (10 Revolutions/pellet). *=p<0.05 compared to the saline control condition
