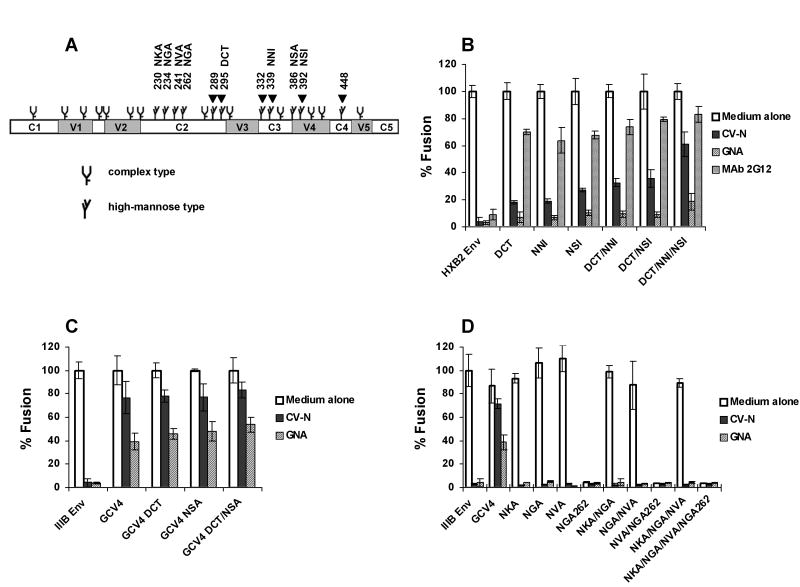
Fig. 3. Defining high-mannose residues on gp120 that affect CV-N antiviral activity.
(A) The schematic of N-linked glycosylation sites on IIIB and HXB2 gp120 according to Leonard et al (Leonard et al., 1990) and Gallaher et al (Gallaher et al., 1995). The constant regions C1, C2, C3, C4 and C5, and the variable regions V1, V2, V3, V4 and V5 are shown. Arrows indicate sites that were changed in CV-N resistant viruses. The fusogenic activity of (B) HXB2 Env and its mutants, (C) IIIB Env, GCV4 and GCV4 mutants, and (D) IIIB Env and its mutants, in the presence or absence of 100 nM CV-N, 400 nM GNA or 25 μg/ml MAb 2G12. The fusogenic activity of each Env in medium alone culture was arbitrarily set to 100%. Data are representative of 3 independent experiments, with each determination performed in triplicate (mean ± SD).